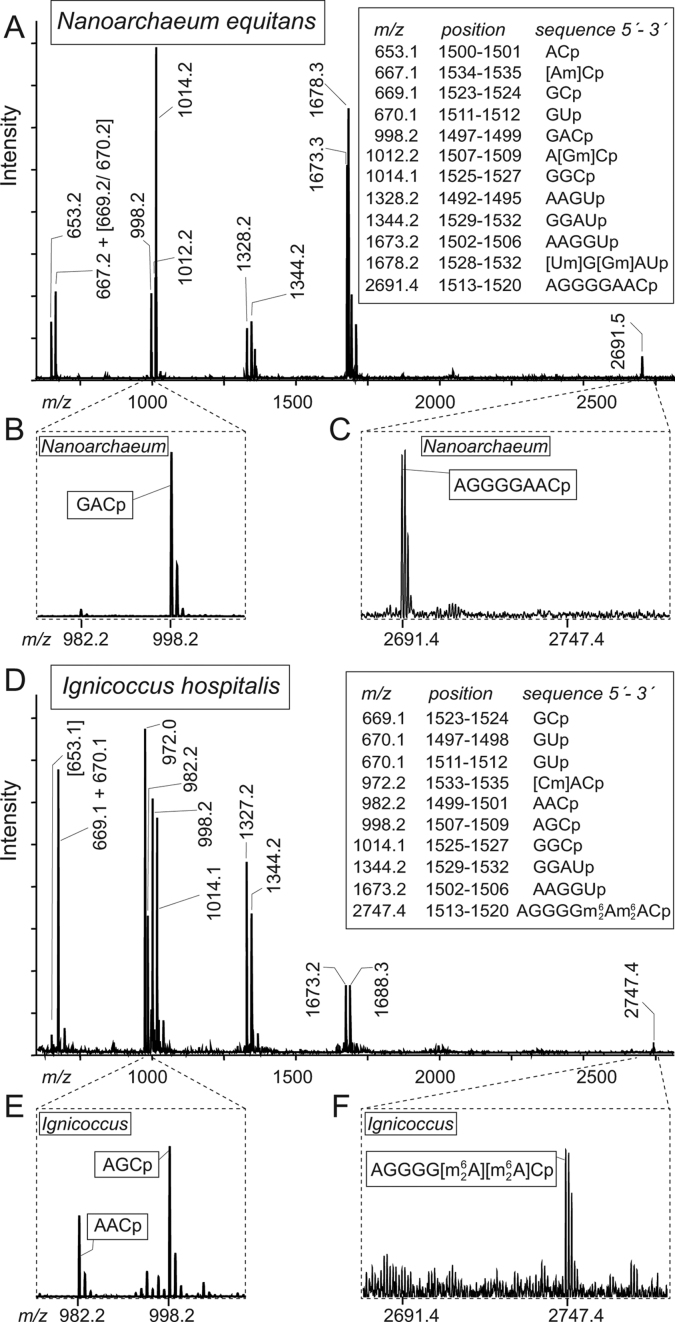
Figure 4.
Analyses of Nanoarchaeum equitans and Ignicoccus hospitalis 16S rRNA fragments containing helix 45. (A) Mass spectrum of RNase A fragments generated from the N. equitans 16S rRNA sequence from nucleotides 1492–1539. The mass/charges (m/z) measured are given above the peaks and matched the theoretical values (box) to within 0.2 Da. (B) Enlargements of the spectrum show that the N. equitans 16S rRNA is virtually clear of I. hospitalis contamination that would give a distinctive AACp fragment at m/z 982.2; and (C) the N. equitans helix 45 loop adenosines are in the fragment AGGGGAACp that flies at m/z 2691.5, indicating that this sequence contains no modification. In addition, several 2΄-O-methylations were evident in this region of the N. equitans 16S rRNA and these are analyzed in detail in Supplementary Figures S2 and S3. (D) The full spectrum from the helix 45 region of 16S rRNA from a pure culture of I. hospitalis. Here, (E) the distinctive AACp fragment is evident, as is (F) the 56 Da increase in mass of the AGGGGAACp fragment indicating that A1518 and A1519 are dimethylated. The additional peaks at m/z 1327 and 1688 arise from modified sequences (Supplementary Figure S3).