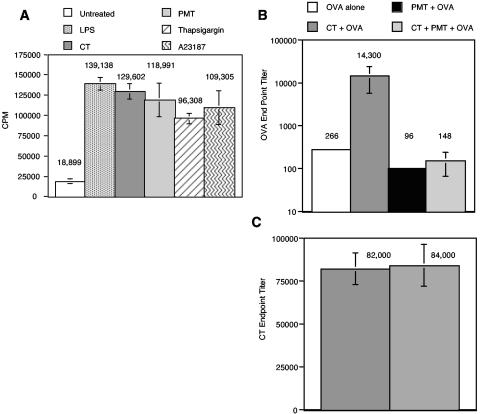
FIG. 3.
A. PMT increases the ability of MDDC to present alloantigen to naïve CD4+ T cells in the allogeneic T-cell response. Naïve CD4+ T cells were plated at 105 cells/well in 96-well U-bottom plates in T-cell medium. MDDC were activated by a 20-h incubation with 1 μg of LPS, CT, or PMT/ml, 10 μM thapsigargin, or 150 ng of A23187/ml. Untreated and activated MDDC were washed, and then 1,000 cells were added to the naïve T cells. Experiments for each condition were performed in triplicate. Proliferation was determined at day 5 by pulsing the cells with 1 μCi of [3H]thymidine per well for the last 18 h of culture. Thymidine incorporation was measured with a Wallac 1450 Microbetta Trilux liquid scintillation counter. Data are means and standard errors for four independent experiments performed on cells mixed from different donors. CPM, counts per minute. B and C. PMT suppress the mucosal adjuvant effects but not the immunogenicity of CT. Groups of five BALB/c mice were orally immunized three times with OVA alone, CT plus OVA, PMT plus OVA, or CT plus PMT plus OVA 2 weeks apart as described in Materials and Methods. Four weeks after the final immunization, the mice were bled, and anti-OVA endpoint titers (A) or anti-CT endpoint titers (B) in the sera of individual mice were determined by ELISA. The means and standard errors of the means are shown.