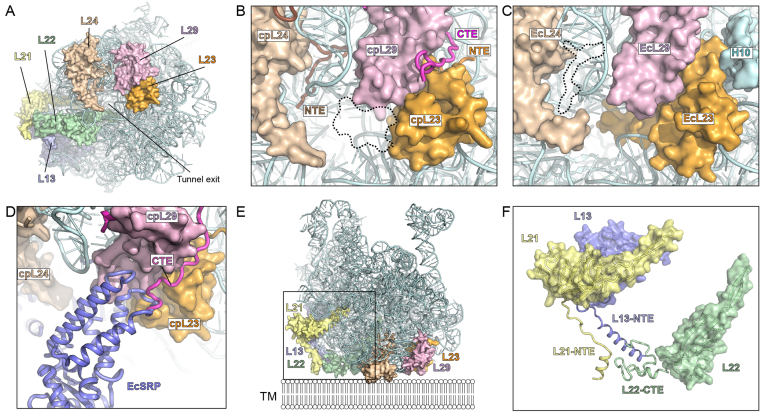
Figure 7.
Interaction of cpRP extensions with rRNA. (A) View onto the tunnel exit site of the chloroplast LSU with rRNA (cyan) and highlighting cpRPs L23 (orange), L29 (purple), L24 (tan), L22 (green), L13 (blue) and L21 (yellow). (B) Zoom of (A) highlighting the NTE of cpL24 and cpL23, and the CTE of cpL29 as well as the shorter β-hairpin of cpL23. (C) Equivalent view of (B) but for Escherichia coli 70S ribosome, highlighting the absence of EcL24-NTE and the presence of the β-hairpin of EcL23 in the tunnel lumen, as well as H10 of Ec23S rRNA. (D) Superimposition of EcSRP (blue) on chlororibosome illustrating overlap with the CTE of cpL29. (E) Chloroplast LSU, colored as in (A), illustrating additional cpRP protein mass that expands the potential surface area of the LSU and facilitates its possible interaction with the thylakoid membrane (TM). (F) Zoom of boxed region in (E) without rRNA to illustrate the contribution of the cpRP extensions (NTE/CTE) of L21 (yellow), L13 (blue) and L22 (green) to the thylakoid membrane interaction surface.