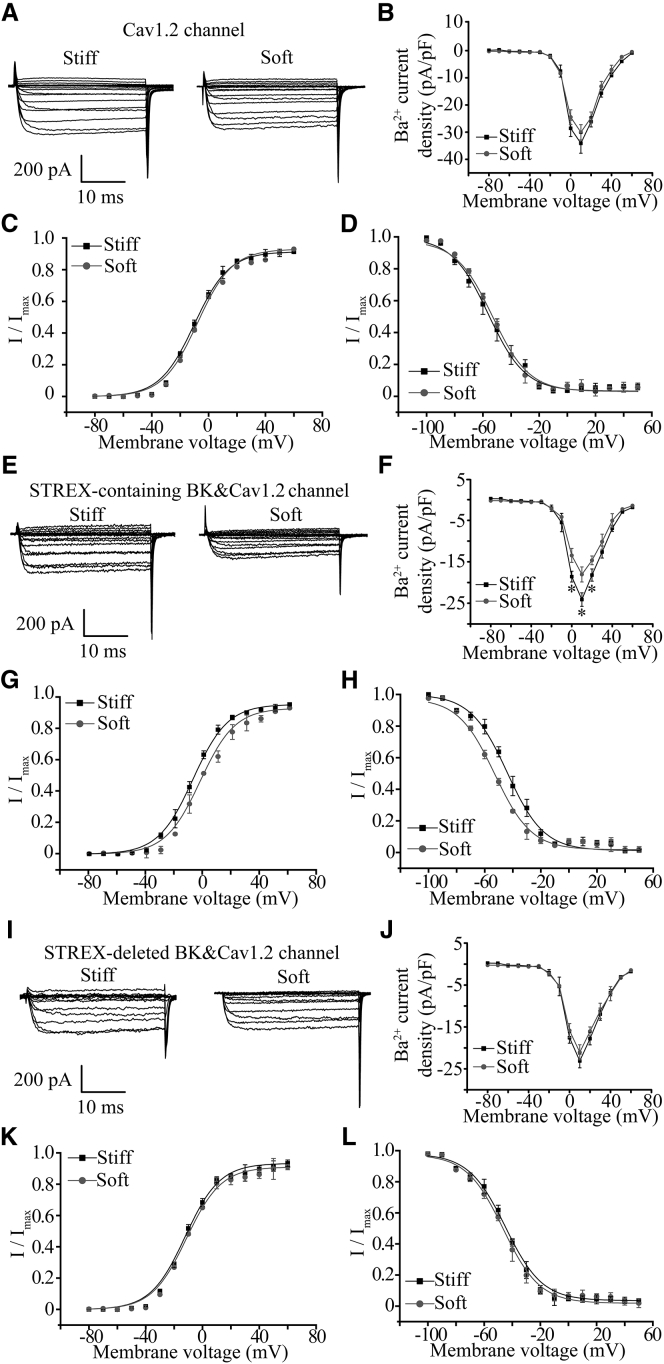
Figure 6.
Regulation of L-type CaV1.2 Ca2+ channel function by substrate stiffness requires the STREX-containing BK channel. (A) Representative whole-cell recordings of Ba2+ currents from HEK293 cells expressing the CaV1.2 channel on the soft and stiff substrates. (B) Summary of the mean I-V relationships from 10 cells in three preparations for each case. (C) Voltage dependence of the CaV1.2 channel activation determined with tail currents from 10 cells for each case. (D) Voltage dependence of the CaV1.2 channel inactivation from recordings in 10 HEK293 cells expressing the CaV1.2 channel in three preparations cultured on the soft and stiff substrates. (E) Representative whole-cell recordings of Ba2+ currents from HEK293 cells coexpressing the STREX-containing BK channel and the CaV1.2 Ca2+ channel on the soft and stiff substrates. (F) Summary of the mean I-V relationships from 12 cells in three preparations for each case. (G) Voltage dependence of the CaV1.2 channel activation determined with tail currents from 12 cells for each case. (H) Voltage dependence of the CaV1.2 channel inactivation from 11 cells in three preparations cultured on the soft and stiff substrates. (I) Representative whole-cell recordings of Ba2+ currents from HEK293 cells coexpressing the STREX-deleted BK channel and the CaV1.2 channel on the soft and stiff substrates. (J) Summary of the mean I-V relationships from 12 cells in three preparations for each case. (K) Voltage dependence of the CaV1.2 channel activation determined with tail currents from 12 cells for each case. (L) Voltage dependence of the CaV1.2 channel inactivation from 11 cells in three preparations cultured on the soft and stiff substrates. ∗p < 0.05, comparison of the current density at the same voltage.