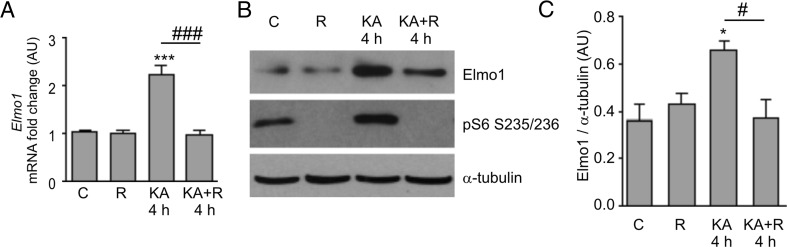
Fig. 4.
Kainic acid-induced Elmo1 expression is mTOR-dependent in cultured cortical neurons. a Results of qRT-PCR-based analysis of Elmo1 expression in cortical neurons cultured in vitro for 5 days and treated as indicated (C control, R rapamycin, KA kainic acid, KA+R KA+rapamycin). The data are presented as mRNA fold changes relative to the control ± standard error (number of cultures N = 5). Significant differences in transcript abundance between the treatments and controls are indicated by asterisks (***p < 0.001). Significant differences in transcript abundance between KA and KA+sR are indicated by hash signs (### p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). b Representative result of Western blot analysis of Elmo1 expression in cortical neurons cultured in vitro for 14 days and treated as indicated. c Quantitative analysis of Western blot of Elmo1 expression levels in cortical neurons cultured in vitro for 14 days and treated as indicated (number of cultures N = 5). α-Tubulin levels were used for normalization. Significant differences in protein abundance between the treatments and controls are indicated by asterisks (*p < 0.05). Significant differences in protein abundance between KA and KA+R are indicated by hash signs (# p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test)