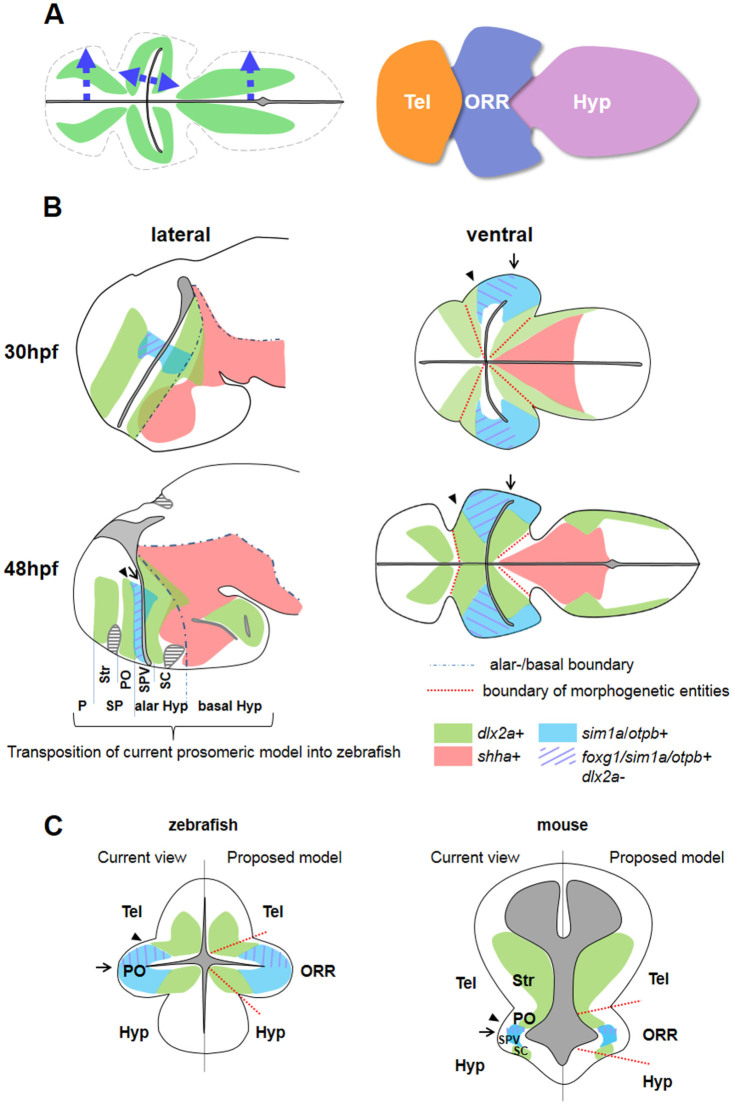
Figure 9. Schematic drawing summarizing the results of this study.
(A): Proposed model of basal forebrain regionalization. The morphogenesis follows the ventricular organization, forming three masses of cells differentiating (green) in the direction of arrows. The secondary prosencephalon thus contains three morphogenetic entities, the telencephalon (Tel), the optic recess region (ORR), and the hypothalamus (Hyp). (B): The expression patterns of several genes examined in this study at 30 hpf and 48 hpf zebrafish embryos, on lateral (left) and ventral (right) views. The black dots in the lateral views represent the alar/basal boundary proposed in the current prosomeric model. The red dotted lines in the ventral view indicate the boundaries of the morphogenetic entities in this study. Annotation on the lateral view at 48 hpf is a transposition from the proposed prosomeric model defined in tetrapods. However, such longitudinal segmentation is not recognizable from the ventral view. Comparison between 30 and 48 hpf also indicates that the regional identity delineated by genes (e.g. SPV by sim1/otp expression) is only transient. (C): Schematic frontal view of zebrafish and mouse forebrain. The gene expression data in mouse is based on previous publications6,41,46,47,66. In the current view (left side) the secondary prosencephalon is divided into the telencephalon and the hypothalamus. However there is a discrepancy in depicting the boundary using developmental genes. The arrow heads indicate the boundary based on Dlx and Sim/Otp expression territories, whereas the arrows indicate the boundary based on Foxg1. Identification of the “preoptic area” (PO) in teleosts and tetrapods are also different. In the proposed model (right side) based on our zebrafish study, the regional boundaries are depicted by apposed differentiated cells originating from different ventricular zones, instead of the gene expression only. Representation of arrows, arrow heads, and the color code for genes are the same in B and C. Abbreviations: Hyp: hypothalamus, ORR: optic recess region, P: pallium, PO: preoptic area, SC: suprachiasmatic area, SPV: supraopto-paraventricular area, SP: subpallium, Str: striatum, Tel: telencephalon.