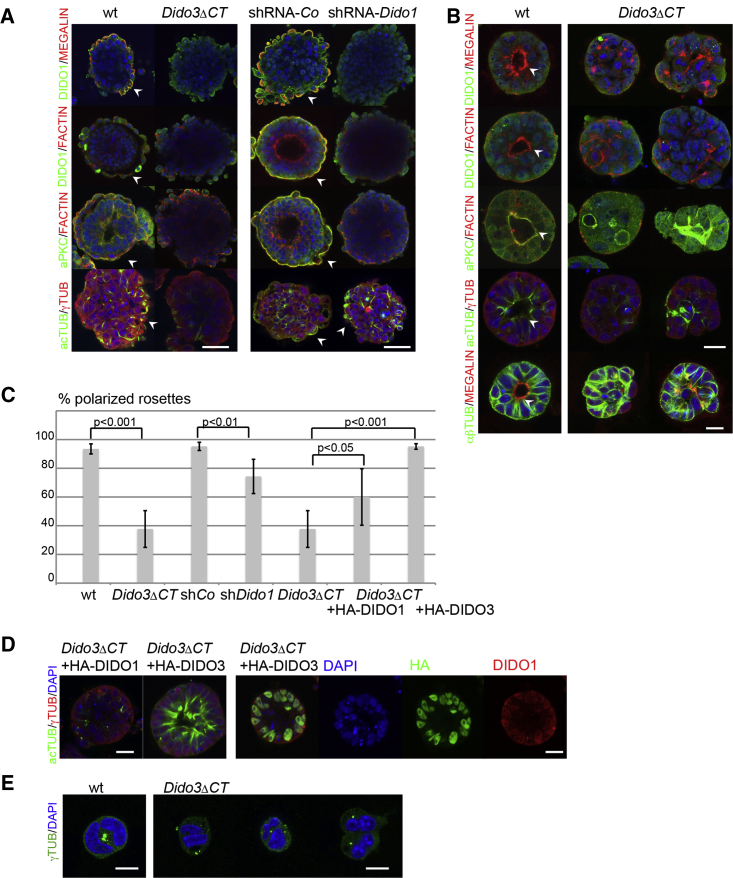
Figure 4.
DIDO3 Regulates Polarization and DIDO1 Regulates Fate of PE Cells
(A) Left: comparison of WT and Dido3ΔCT d4EBs for apical polarization markers (MEGALIN, red; phalloidin-labeled F-ACTIN, red; aPKC, green; acetylated TUBULIN; green) and DIDO1 (green) at the PE layer (arrowheads). Right: comparison of shRNA-control and shRNA-Dido1 d4EBs (staining as in left panel). Scale bars, 50 μm.
(B) Left: WT rosettes stained for polarization markers as in (A) and DIDO1 for apical polarization at the central lumen (arrowheads). Right: examples of Dido3ΔCT rosettes with mislocalization of polarization markers; bottom row of rosettes stained with anti-αβ-TUBULIN (green). Nuclei (DAPI, blue). Scale bars, 20 μm.
(C) Quantification of the percentage of polarized rosettes of WT, Dido3ΔCT, shRNA-Co, shRNA-Dido1, HA-DIDO1-reconstituted Dido3ΔCT, and HA-DIDO3-reconstituted Dido3ΔCT. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n from more than three independent experiments).
(D) Left: acetylated TUBULIN (green) in Dido3ΔCT rosettes reconstituted with HA-DIDO1 or HA-DIDO3. Right: HA-DIDO3 (green) and DIDO1 (red) localization in HA-DIDO3-reconstituted Dido3ΔCT rosettes. Scale bars, 20 μm.
(E) Position of centrosomes labeled with anti γ-TUBULIN (green) in WT (left) and Dido3ΔCT 2-cell stage rosettes (right). Nuclei (DAPI; blue). Scale bars, 10 μm.