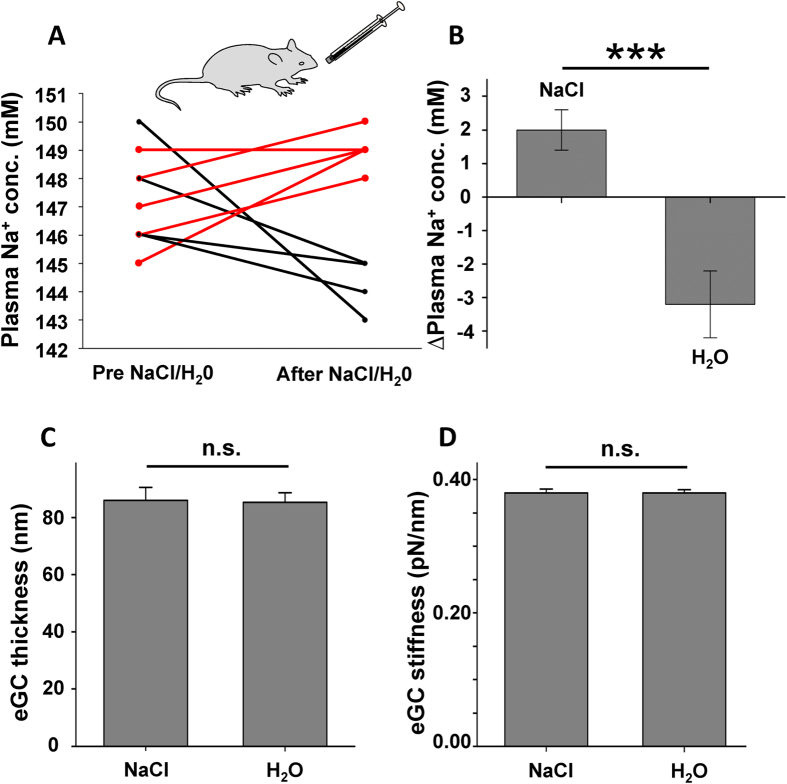
Figure 5. Acute oral salt challenge increases the plasma Na + concentration.
(A) Plasma Na+ concentrations were measured after oral application of salt/glucose solution or water with a stomach tube in the blood plasma of wild-type mice. 30 minutes after the treatment the salt/glucose uptake resulted in an increased plasma Na+ concentration while water intake decreased the plasma Na+ concentration. (B) Differences between the plasma Na+ concentration before and after salt/glucose or water intake (N = 5, *** indicates p ≤ 0.001). No acute effects of salt/glucose intake on the thickness (C) and stiffness (D) of the endothelial glycocalyx could be observed in ex vivo endothelial cells of aorta preparations measured with the AFM (N = 5, n = 81–90).