Figure 4.
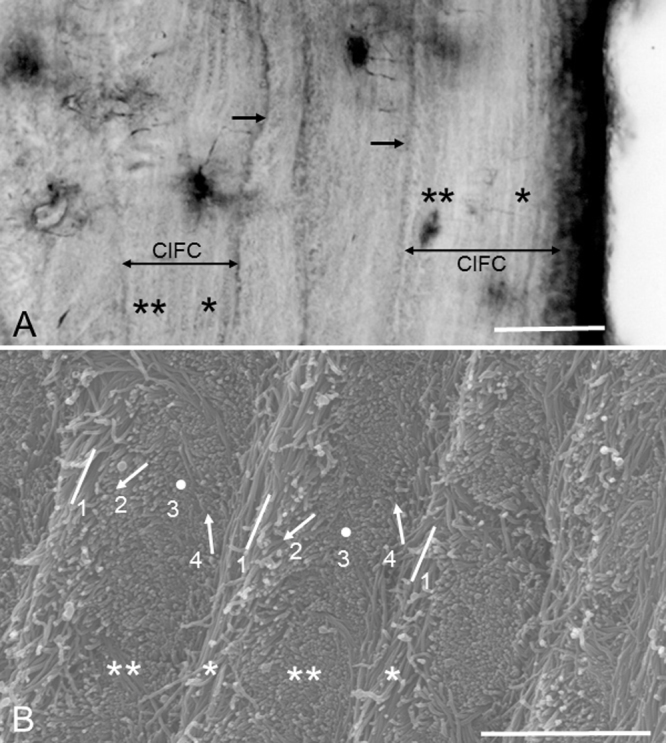
(A) Magnification of extrinsic fiber-free CIFC partitioned by incremental lines (arrows). In CIFC an alternation of darkly and faintly stainable lamellae is obvious on the periodontal ligament side (*) and non-obvious on the dentin side (**). Bar 30 μm. Hematoxylin-stained ground section. (B) Scanning electron micrograph showing the alternating lamellae. The specimen (a mandibular molar) has been treated by 10% NaOH maceration method to observe individual collagen fibrils clearly. Two types of lamellae, i.e. lamellae of longitudinally and near-longitudinally cut fibril arrays (*) and lamellae of transversely and near-transversely cut fibril arrays (**) create the alternating lamellae. Four types of fibril arrays are roughly recognized: 1, longitudinally cut fibril arrays; 2, obliquely cut fibril arrays facing downward; 3, transversely cut fibril arrays; 4, obliquely cut fibril arrays facing upward. As traced from left to right, the fibril arrays appear to rotate clockwise. Bar 3 μm.
