Fig. 3.
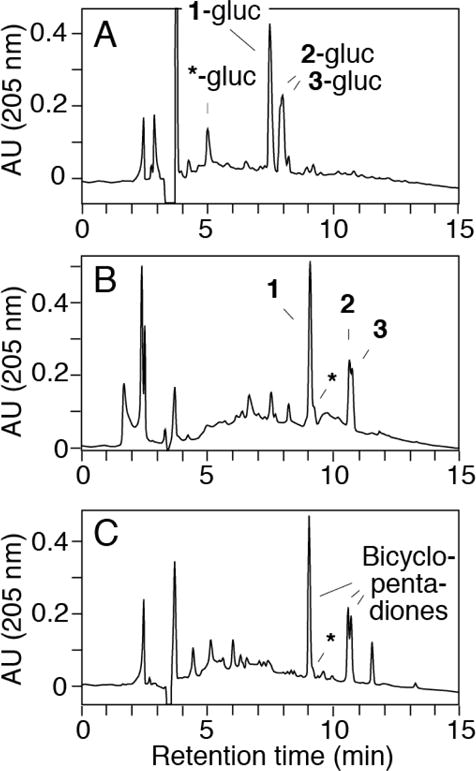
RP-HPLC analysis of the transformation of curcumin-glucuronide by horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and H2O2. (A) Analysis of products from the reaction of curcumin-glucuronide (25 μM) with HRP (0.01 U/ml) and H2O2 (40 μM). (B) The sample was reanalyzed after hydrolysis with β-glucuronidase (pH 4, 1 h at 37°C). (C) Curcumin (30 μM) was reacted with HRP and H2O2. The asterisk indicates the elution of vanillin as the glucuronic acid conjugate (in A) or the free compound (in B and C). Samples were analyzed using a Waters Atlantis T3 5 μm column (250 × 4.6 mm) eluted with a gradient of 20% to 80% acetonitrile in water (0.05% acetic acid) within 20 min at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Product elution was monitored using a diode array UV detector, and chromatograms recorded at 205 nm are shown.
