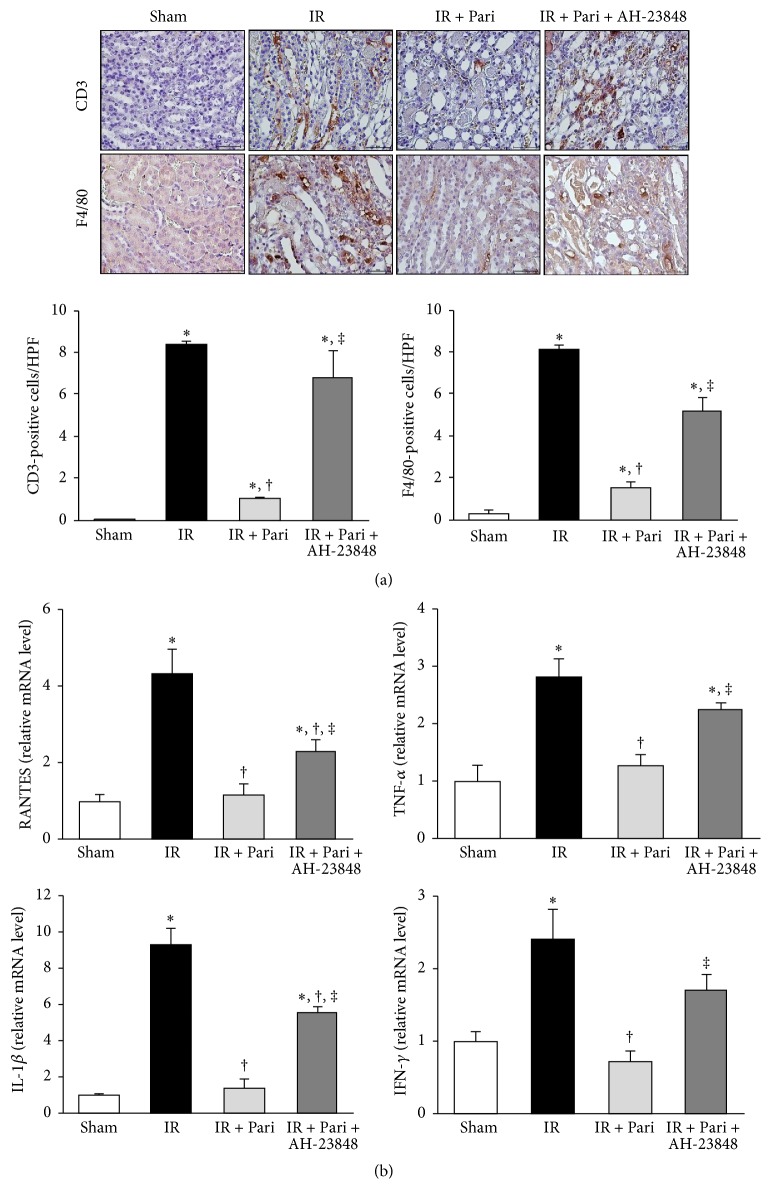
Figure 10.
Paricalcitol prevented inflammatory cell infiltration and suppressed the expression of inflammatory cytokines via an EP4-dependent pathway in mice kidney with ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury. (a) The infiltration of CD3+- and F4/80+-expressing cells was examined by immunohistochemical staining. The number of CD3+- and F4/80+-positive cells was increased significantly in mice kidney with IR injury, and this increase was ameliorated by paricalcitol. AH-23848 cotreatment significantly reversed the effect of paricalcitol on inflammatory cell infiltrations into the ischemic kidney. Original magnification ×400. (b) RT-PCR analysis showed that the mRNA levels of RANTES, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFN-γwere elevated in mice kidney with IR injury. Paricalcitol suppressed the IR-induced overexpression of these inflammatory cytokines and cotreatment with AH-23848 reversed all of these suppressive effects. ∗P < 0.05 versus sham group, †P < 0.05 versus IR group, and ‡P < 0.05 versus IR + Pari group; n = 6–8 for each group. Bar = 50 μm.