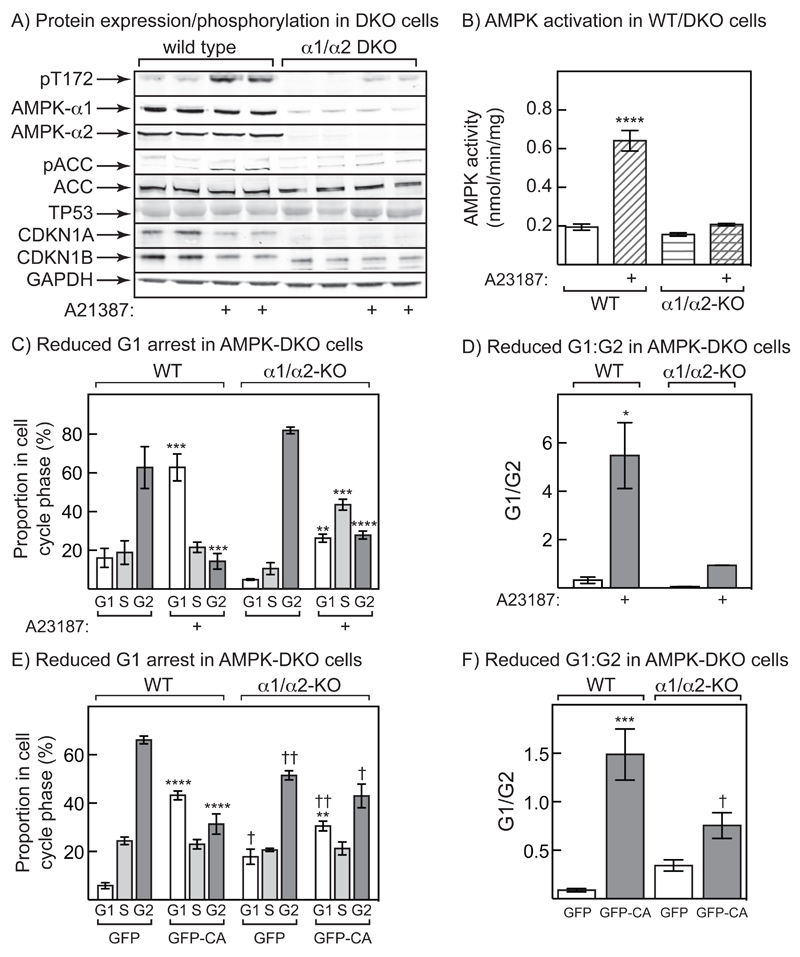
Figure 6. Cell cycle arrest by A23187 in G361 cells is AMPK-dependent.
(A) Expression and phosphorylation of proteins in wild type (WT) and α1/α2 double knockout (DKO) cells derived from G361 cells using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Phosphorylation of AMPK, ACC and Raptor, and expression of AMPK-α1, -α2, ACC, Raptor, TP53, CDKN1A and CDKN1B, was assessed in cells treated with and without 0.3 μM A23187 for 24 hr. (B) AMPK activity in WT and DKO cells treated with and without 0.3 μM A23187 for 24 hr. Significant differences between A23187- and vehicle-treated samples, determined by 2-way ANOVA, are indicated: ****p<0.0001. (C) Cell cycle analysis in cells treated with 0.3 μM A23187 for 24 hr, then with nocodazole for a further 24 hr. The proportion of cells in each cell cycle phase was determined by flow cytometry of cells stained with propidium iodide. Significant differences in each cell cycle phase between A23187- and vehicle-treated samples, determined by 2-way ANOVA, are indicated: **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (D) Results from the experiment shown in (C) but expressed as ratios of G1:G2 phases. Significant differences between A23187- and vehicle-treated samples, determined by 2-way ANOVA, are indicated: p<0.05. (E) Cell cycle analysis in WT or DKO cells transfected with DNA encoding GFP or GFP-CA.for 24hr, then with nocodazole for 24 hr. Significant differences in each cell cycle phase between GFP and GFP-CA-transfected samples (**p<0.01; ****p<0.0001), and between WT and DKO samples (†p<0.05, ††p<0.01) are indicated. (F) Same data as (E), but analysing G1:G2 ratios. Significant differences between GFP and GFP-CA-transfected samples (***p<0.001), and between WT and DKO samples (†p<0.05) are indicated.