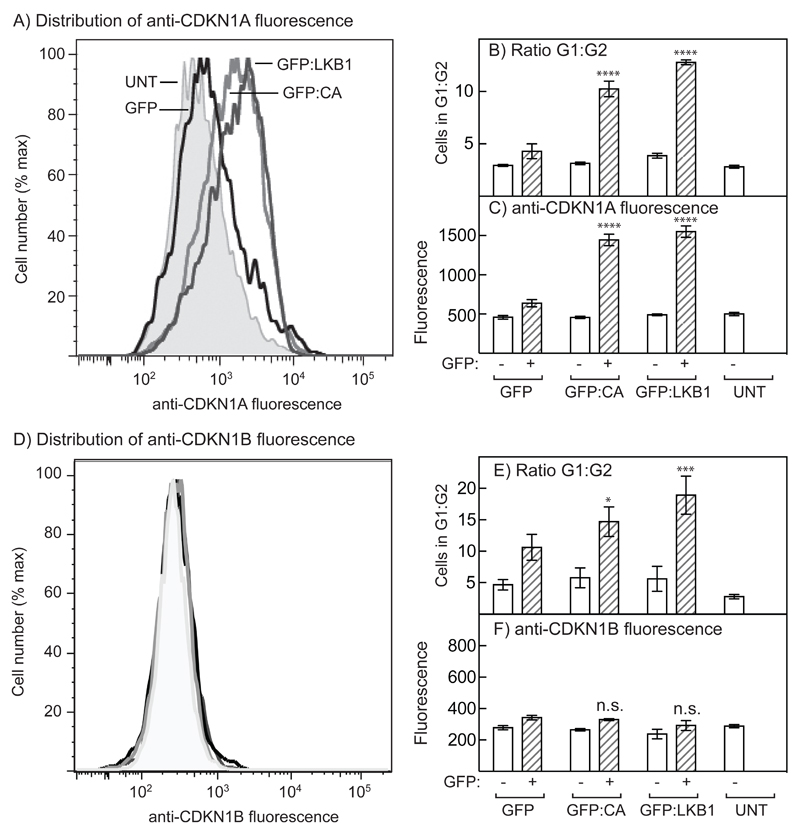
Figure 7. AMPK activation in G361 cells induces increased expression of CDKN1A but not CDKN1B, and cell cycle arrest.
G361 cells were transiently transfected with DNAs encoding GFP, GFP-LKB1 or GFP-CA. (A) Distribution of CDKN1A expression using anti-CDKN1A antibody in untransfected cells (UNT) and in cells expressing GFP, GFP-LKB1 or GFP-CA. (B) Ratios of G1:G2 phases in cells not expressing GFP (open bars), or in cells from the same dish expressing GFP, GFP-LKB1 or GFP-CA (hatched bars); significant differences by 2-way ANOVA from controls expressing GFP alone are shown: ****p<0.0001 (n = 4). (C) Expression of CDKN1A by flow cytometry in the same cells analysed in (B); significant differences by 2-way ANOVA from controls expressing GFP alone are shown: ****p<0.0001 (n = 4). (D) Distribution of CDKN1B expression using anti-CDKN1B antibody in untransfected cells (UNT) and in cells expressing GFP, GFP-LKB1 or GFP-CA; the grayscale coding is as in 1A and there are no significant differences. (E) Ratios of G1:G2 phases in untransfected cells (open bars), or in cells from the same dish expressing GFP, GFP-LKB1 or GFP-CA (hatched bars); significant differences by 2-way ANOVA from controls expressing GFP alone are shown: *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 (n = 4). (F) Expression of CDKN1B by flow cytometry in the same cells analysed in (E); there were no significant differences (n = 4).