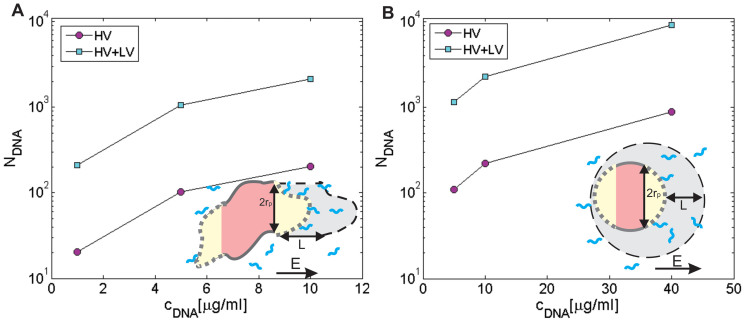
Figure 4. Theoretical analysis of DNA accumulation at the cell membrane due to electrophoretic force.
The number of DNA molecules (NDNA) available for contact with the permeabilized part of the cell membrane for different plasmid cDNA for plated cells (A) and cells in a suspension (B) are shown for HV and HV+LV pulses (corresponding transfection efficiencies are shown in Fig 1). The schematic representation shows the calculation of NDNA, where L is the distance traveled due to electrophoresis and rp is the radius of the permeabilized membrane (dotted, yellow area) for plated cells (A) and cells in a suspension (B). The gray shaded region represents the volume V from which DNA molecules are brought in contact with the cell membrane. The strength and length of pulses determine the distance L from which DNA can access the cell membrane (gray) and E determines the area of the membrane which is electropermeabilized.