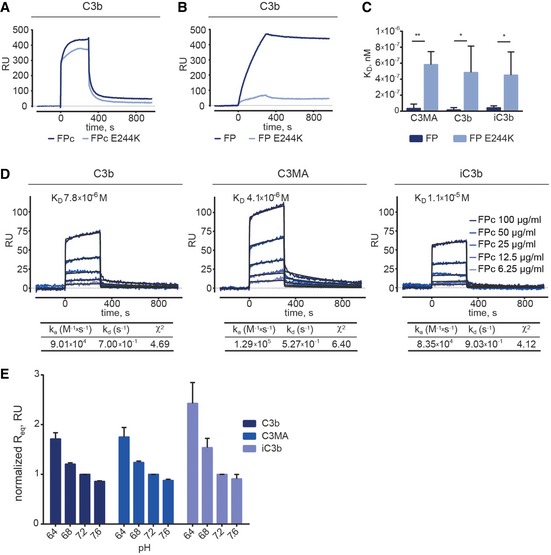
Figure 3. Binding of FP and FPc (wild type or E244K) to C3 products analyzed by surface plasmon resonance.
-
A, BSPR analysis of FPc and FPc E244K (20 μg/ml) on immobilized C3b showing that they bind similarly to C3b (A). In contrast, non‐cleaved FP E244K (2.5 μg/ml) bound much weaker to immobilized C3b compared to wild‐type recombinant FP (B).
-
CComparison of KD values observed for FP and FP E244K at 5.0, 2.5, and 1.25 μg/ml upon binding to C3MA, C3b, and iC3b confirms the functional defect of the mutant.
-
DA detailed kinetic SPR analysis using FPc at concentrations ranging from 6.25 to 100 μg/ml. FPc was injected on the C3b/C3MA/iC3b‐coated chip for 300 s followed by 600 s dissociation. The KD values were calculated using a 1:1 interaction model assuming a conformational change upon ligand‐analyte binding.
-
ESPR experiments with wt FPc injected at 100, 50, and 25 μg/ml over immobilized C3b, C3MA, and iC3b at different pH values. The calculated Req values are normalized to Req at pH 7.2.
