Figure 4. PRC2 interacts with RNA with low specificity.
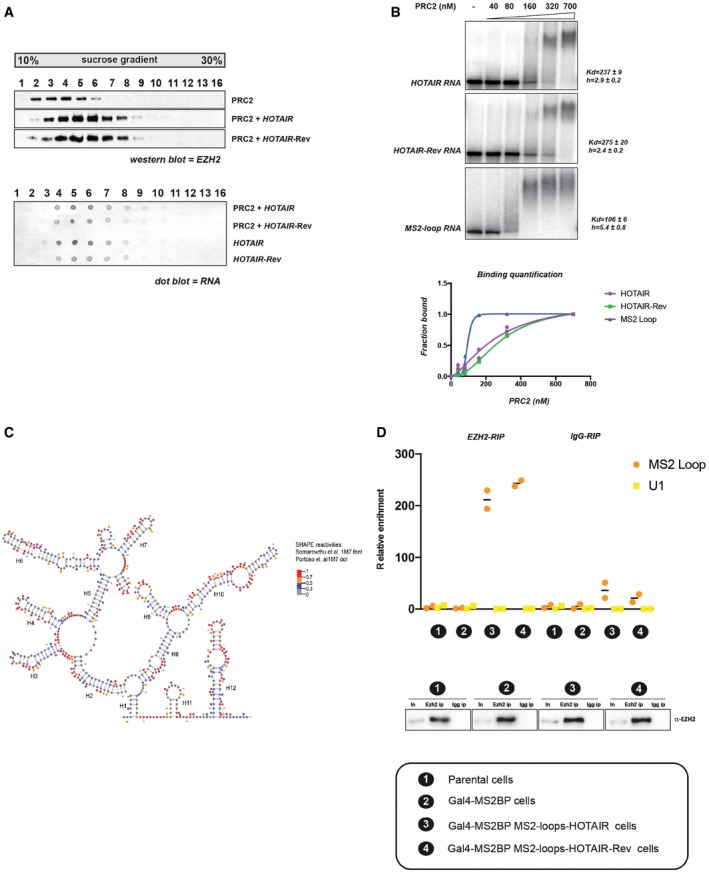
- PRC2 was incubated with or without biotinylated HOTAIR or HOTAIR reverse‐complement RNAs and analyzed by density gradient centrifugation on a linear sucrose gradient (10–30%). Individual fractions collected from sucrose gradient were probed by Western blot for EZH2 (upper panel) or by dot blot for biotinylated RNA (lower panel).
- Representative EMSA experiments showing binding of PRC2 to full‐length HOTAIR, HOTAIR‐Rev and MS2 loop RNA probes. Equilibrium dissociation constant (K d) values and Hill slope are calculated on biological replicates (n = 2). Corresponding binding curves of biological duplicate EMSA experiments (bottom panel).
- Predictive secondary structure for the first 530 bp of HOTAIR RNA from the RNAstructure software and VARNA visualization software. HOTAIR D1 domain as modeled by Somarowthu et al (2015) according to SHAPE‐CE probing is shown. SHAPE reactivities from Somarowthu et al (2015) are depicted by colored nucleotides; 1M7 SHAPE reactivity obtained in our experiment is represented by colored dots over the nucleotides. Highly reactive nucleotides are displayed in red and orange, and low reactive nucleotides are displayed in black or blue according to the values reported in the legend.
- EZH2 binds both MS2‐HOTAIR and MS2‐HOTAIR‐Rev RNAs in vivo. RIP experiments with EZH2 antibody in cell models indicated on the x‐axis. MS2 loop and U1 primers were used in qRT–PCR. Y‐axis represents relative enrichment (individual experiments and mean, n = 2). Input (In) and IP were loaded and probed with EZH2 antibody (lower panel). Correspondence between numbers and model cell lines is indicated at the bottom.
Source data are available online for this figure.
