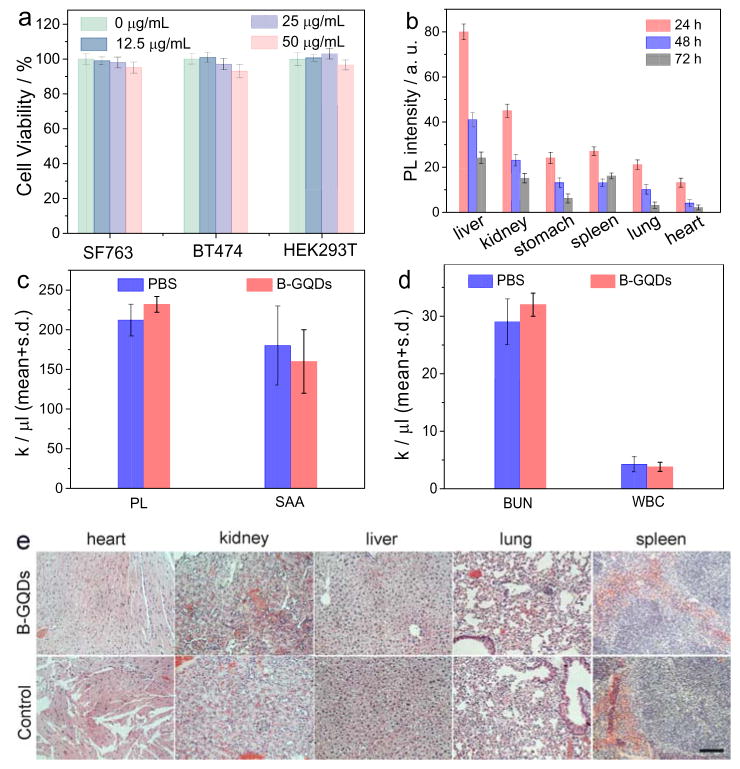
Figure 3.
In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility assessment of B-GQDs. (a) In vitro cytotoxicity study of B-GQDs performed by assessing the viability of SF763, BT474 and HEK293T cells 72 h after treatment with B-GQDs. (b) Distributions of B-GQDs in various organs and tissues of nude mice receiving B-GQDs, determined at various time points post-injection. Assessment of toxic effects of B-GQDs on liver and kidney by hematology analysis. (c) platelet (PL) levels and serum alanine aminotransferase (SAA) levels, (d) blood urea nitrogen levels (BUN) and white blood (WBC) cells of mice receiving B-GQDs or PBS injection, measured 24 h after administration (standard deviation of mean, n = 4 mice per treatment). (e) H&E stained tissue sections of mouse heart, kidney, liver, lung and spleen, obtained from non-injected animals (bottom row, control) and those injected with B-GQDs at a concentration of 1 mg mL−1 (top row). The scale bar is 125 μm.