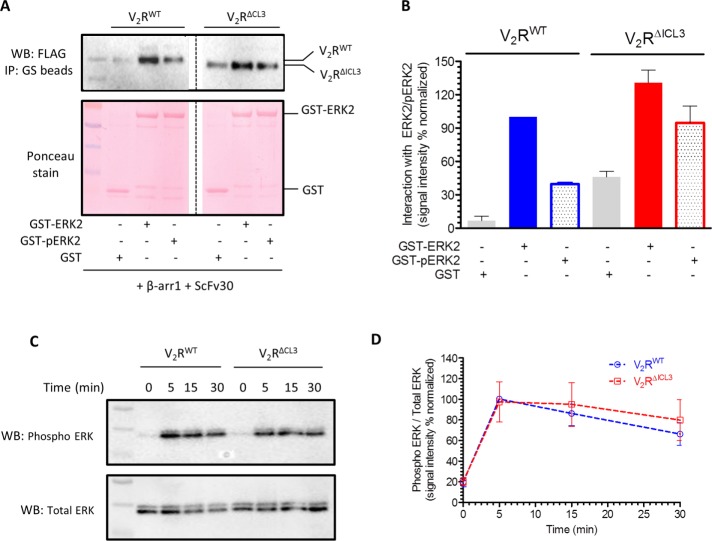
FIGURE 5:
V2RΔICL3-βarr1 complex binds ERK2, and V2RΔICL3 exhibits efficient ERK activation. (A) V2RΔICL3-βarr1 complex interacts efficiently with inactive (i.e., nonphosphorylated) and active (i.e., phosphorylated) ERK2, similar to V2RWT-βarr1 complex, as assessed by a coIP experiment. Here ScFv30 is used to stabilize V2R-βarr1 complexes to avoid any potential clash with ERK2 binding. Purified GST is used as negative control. Representative image of three independent experiments. (B) Densitometry-based quantification of coIP data presented in A, showing the interaction of inactive and active ERK2 with preformed V2RWT/ΔICL3-βarr1 complexes. Data are normalized with respect to the signal observed for the interaction of inactive ERK2 with V2RWT-βarr1 complex (treated as 100%). (C) Agonist (100 nM AVP)-stimulated ERK activation in HEK-293 cells expressing V2RWT or V2RΔICL3 as measured by Western blotting. V2RΔICL3 exhibits efficient ERK activation similar to V2RWT, indicating that the lack of core interaction with βarr does not influence ERK phosphorylation. A representative image from six independent experiments. (D) Densitometry-based quantification of agonist-induced ERK phosphorylation in C. Data represent average ± SEM of six independent experiments normalized with respect to signal at 5 min for V2RWT (treated as 100%).