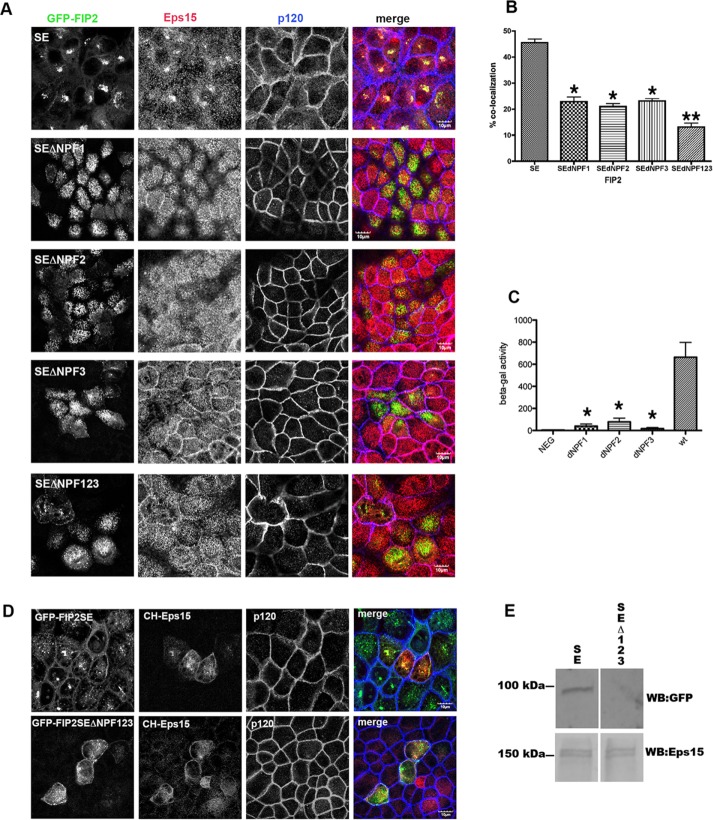
FIGURE 3:
Mutation of all three NPF domains or any individual NPF domain of FIP2 released Eps15 from the GFP-FIP2(S227E) compartment. (A) The GFP-FIP2(S227E) MDCK cell lines with or without the NPF domain mutations were plated onto glass coverslips, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and stained for Eps15 (red in merge) and F-actin (phalloidin; blue in merge). Bar, 5 μm. (B) Manders quantification of the colocalization shown in A; minimum of 30 cells per cell line were counted. The GFP-FIP2(S227E) containing any of the NPF domain mutations (SEdNPF1, SEdNPF2, or SEdNPF3) exhibited a significant loss of colocalization compared with GFP-FIP2(S227E). Mutation of all three NPF domains (SEdNPF123) elicited a further significant decrease in colocalization. *p < 0.05 by Dunn’s test vs. SE. **p < 0.05 vs. all other groups. (C) Results of yeast two-hybrid assay. The amount of β-galactosidase activity was calculated by compassion to a standard curve of known β-galactosidase concentrations. The assay was performed three separate times. NEG, negative control. The GFP-FIP2(S227E) containing any of the NPF domain mutations exhibited a significant loss of colocalization compared with GFP-FIP2(S227E). *p < 0.05 by Dunn’s test. (D) GFP-FIP2(S227E) and GFP-FIP2(S227EΔNFP123) MDCK cells were transfected mCherry-Eps15, fixed, and stained for p120 (blue in merge). mCherry-Eps15 was localized with the GFP-FIP2(S227E) but not with coexpressed GFP-FIP2(S227ΔNPF123). (E) Western blot of mCherry-Eps15 precipitated from GFP-FIP2(S227) or GFP-FIP2(S227ΔNPF123)–expressing cells. The blot was probed simultaneously for GFP (top) and Eps15 (bottom) and imaged on a LiCor Odyssey FC imager. Size makers are shown on the left.