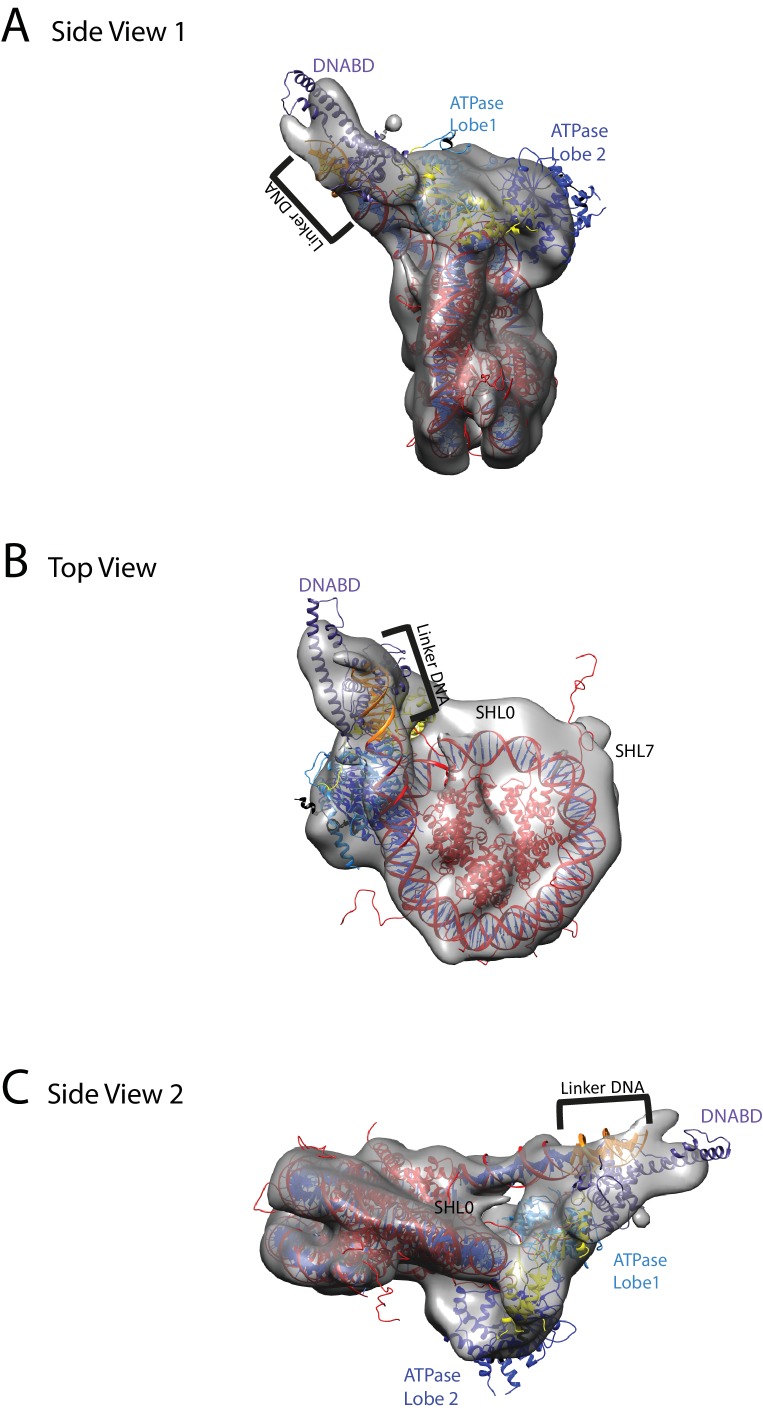
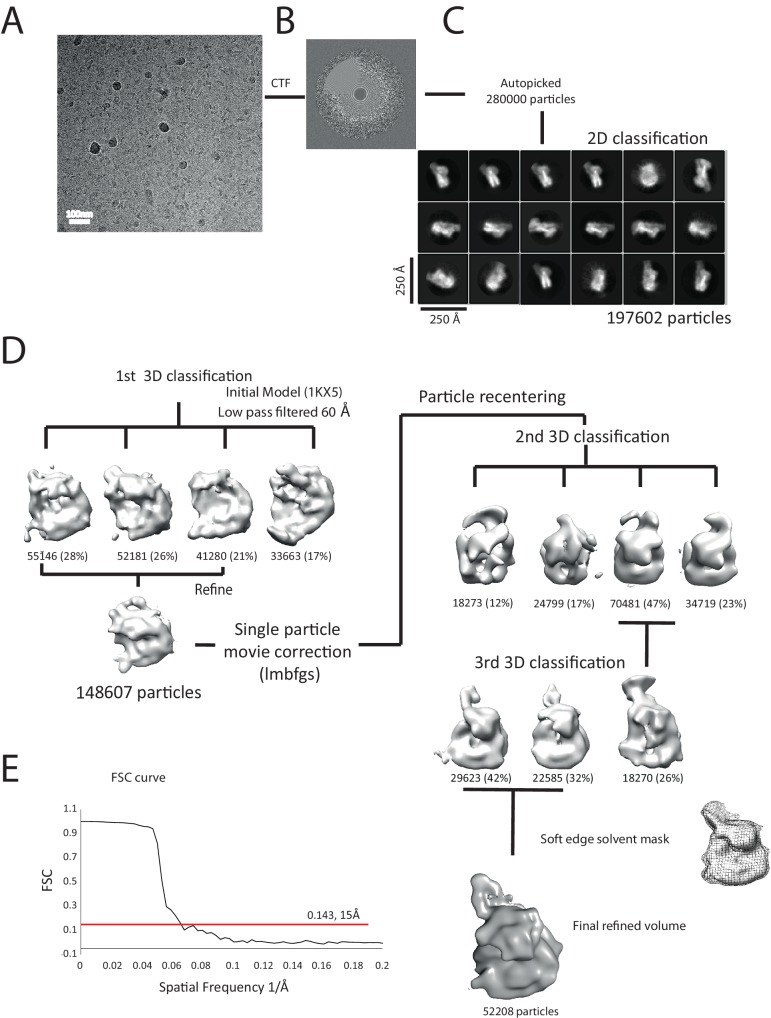
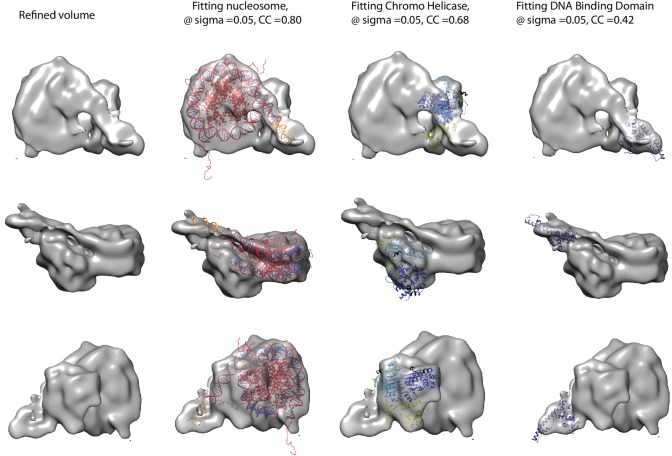
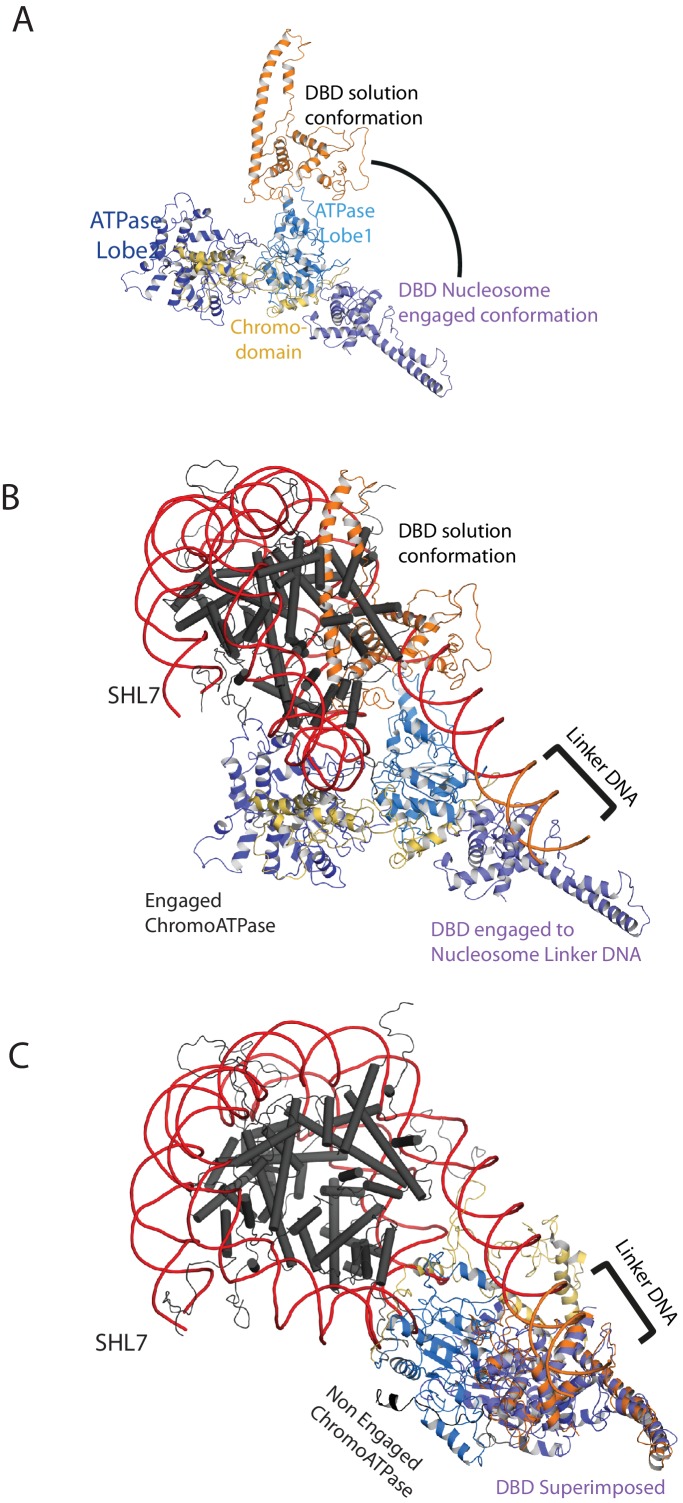
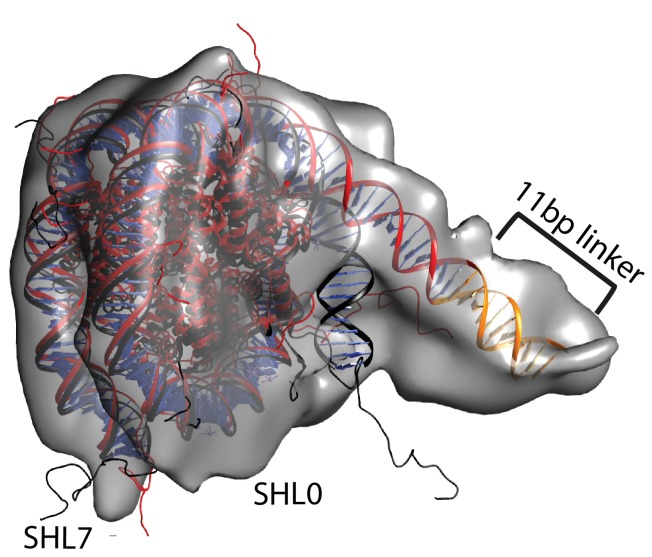
Figure 7. Chd1 bound to nucleosomes via its DNA binding and ATPase domains.
(A) Side view 1 of the electron density map shown in semi-transparent grey surface with docked nucleosome (red, 1KX5) and the Chd1, chromoATPase (3MWY) and DNA-binding domain (3TED) crystal structures shown in cartoon representation. The various domains of Chd1 are labelled. ATPase lobe1 in marine, ATPase lobe2 in blue, chromo domain in yellow and the DNA-binding domain in deep blue. The 11 bp DNA linker region defined in the electron density map is coloured orange and indicated. (B) Top view of the nucleosome-bound Chd1 complex. The dyad axis of the nucleosome is labelled as SHL0 (super helical location 0) and edge of the nucleosome is indicated as SHL7. (C) Side view 2 of the nucleosome-Chd1 complex.