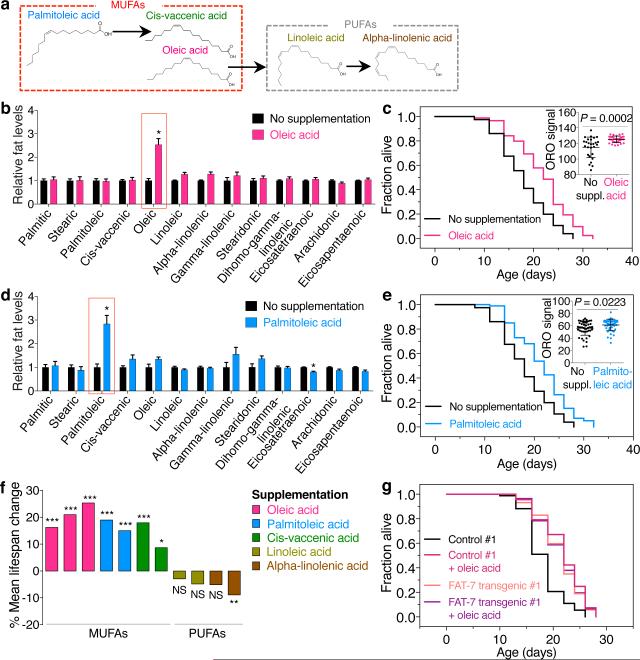
Figure 5. Dietary supplementation of MUFAs is sufficient to extend lifespan.
a, Chemical structure of fatty acids used in supplementation experiments. b, GC-MS. Mean ± s.e.m. of 3 independent experiments, each with 2-3 biological replicates. c, Oleic acid supplementation extends lifespan in wild-type worms (P < 0.0001, log-rank). Inset: ORO quantification. Mean ± s.d., n ≥ 27 worms per condition. d, GC-MS. Mean ± s.e.m. of 2 independent experiments, each with 2-3 biological replicates. e, Palmitoleic acid supplementation extends lifespan in wild-type worms (P < 0.0001, log-rank). Inset: as in c, n ≥ 45 worms per condition. f, Mean lifespan changes in independent supplementation experiments (P values: log-rank). g, FAT-7 overexpression extends lifespan (P < 0.0001, log-rank), which is not further extended by dietary oleic acid. P values: Two-tailed Mann-Whitney (Benjamini-Hochberg correction for > 1 comparison). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.