Extended Data Figure 4. Role of SBP-1/SREBP, MDT-15/MED15, NHR-49, and NHR-80 in the fat accumulation and longevity of H3K4me3-methyltransferase deficient worms.
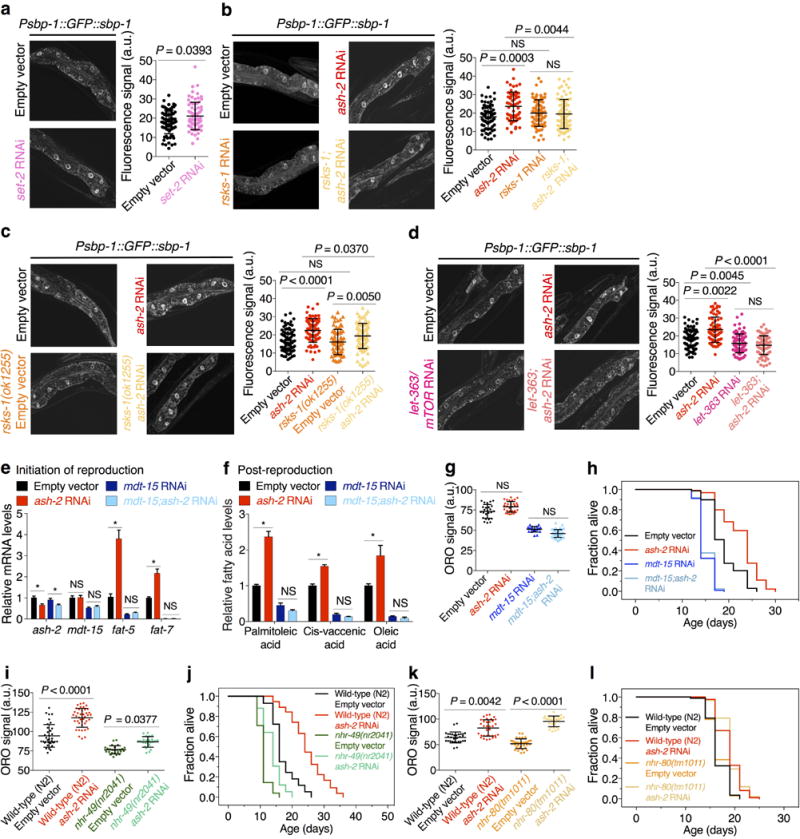
a-d, Images and quantification of SBP-1 nuclear accumulation. Mean ± s.d. of 2 independent experiments, each with 4-6 nuclei per worm of ≥ 8 worms per condition. e, RT-qPCR. Mean ± s.e.m. of 2 independent experiments, each with 3 biological replicates. f, GC-MS quantification of MUFAs. Mean ± s.e.m. of 2 independent experiments, each with 2-3 biological replicates. g, ORO quantification. Mean ± s.d., n ≥ 21 worms per condition. h, ash-2 RNAi extends lifespan in wild-type worms (P < 0.0001, log-rank), but not in mdt-15 RNAi worms. i, ORO quantification, Mean ± s.d., n ≥ 24 worms per condition. j, ash-2 RNAi extends lifespan in both wild-type worms and nhr-49(nr2041) mutants (P < 0.0001, log-rank). k, ORO quantification. Mean ± s.d., n ≥ 27 worms per condition. l, ash-2 RNAi extends lifespan in both wild-type worms and nhr-80(tm1011) mutants (P < 0.0001, log-rank). i-k, Representative of 2 experiments. P values: a, Two-tailed Mann-Whitney; b-d, g, i, k, Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn's correction; e-f, Two-tailed Mann-Whitney with Benjamini-Hochberg correction. * P < 0.05.
