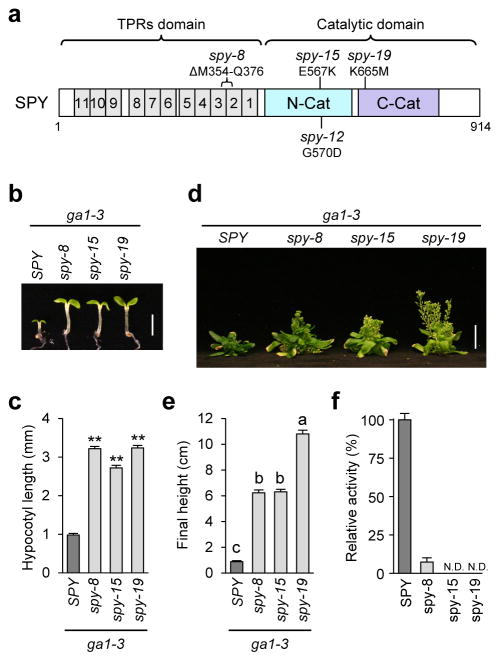
Figure 3. Phenotype and enzyme activity analyses of the spy mutants.
(a) Schematic of SPY protein structure. Mutation in spy-8 is located in TPR2-3, whereas mutations in spy-12, spy-15 and spy-19 are located in the C-terminal catalytic domain. (b–c) All spy alleles rescued the hypocotyl growth defect of the GA-deficient mutant ga1-3. Hypocotyl lengths of 6d-old seedlings grown in short-day conditions were measured. In (b), bar = 2.5 mm. In (c), average hypocotyl lengths are means ± SE. n=20. ** p<0.01, significantly different from WT. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-tests. Three biological replicates were analyzed with similar results. (d) Photo of 67-day-old plants. bar = 2 cm. (e) Average final heights of ga1-3 and ga1-3 spy mutants. The data are means ± SE. n=13. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences, p<0.01. Two biological replicates were analyzed with similar results. In (d–e), plants were grown under 16 hr-light conditions. (f) Malachite green-coupled assay shows that spy-8 retains a low POFUT activity, but no activity was detected for spy-15 or spy-19. Truncated 3TPR-SPY and -spy proteins were expressed and purified as His10-MBP fusion proteins for this assay using RGApep1 and GDP-fucose as substrates. Means ± SE are shown. Three biological replicates were analyzed with similar results. The immunoblot detected by anti-SPY antibodies indicates that similar amounts of WT and mutant enzymes were used in the assays (Supplementary Fig. 8a).