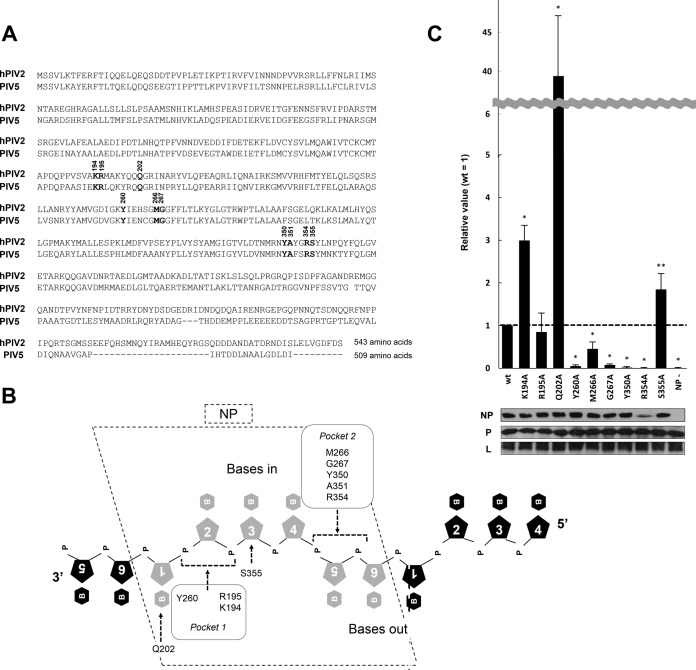
FIG 1.
Mutagenesis analysis using the hPIV2 Rluc minireplicon assay for amino acids in the putative RNA-binding domain of NP. (A) Comparison of hPIV2 and PIV5 NP amino acid sequences. Bold numbers over the nucleotides indicate amino acids responsible for RNA binding. The accession numbers are BAE00051 and YP_138511 for hPIV2 and PIV5, respectively. (B) Schematic diagram representing the putative binding of amino acids in the NP with ribonucleotides. The pentagons with numerals and hexagons with “B” and “P” represent ribose, base, and phosphate, respectively. Amino acids included in two RNA-binding pockets estimated by the PIV5 NP structure are indicated. (C) Relative Rluc activity in the minireplicon assay with the hPIV2 polymerase complex including NP mutants. The Rluc expression from minigenomes is normalized to internal control Fluc expression, and relative values are shown (NPwt = 1). NP−, result for the Rluc minigenome without NP plasmid. Data represent means and standard deviations from triplicate experiments. Expression of NP, P, and L was detected by Western blotting using specific MAbs. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.05.