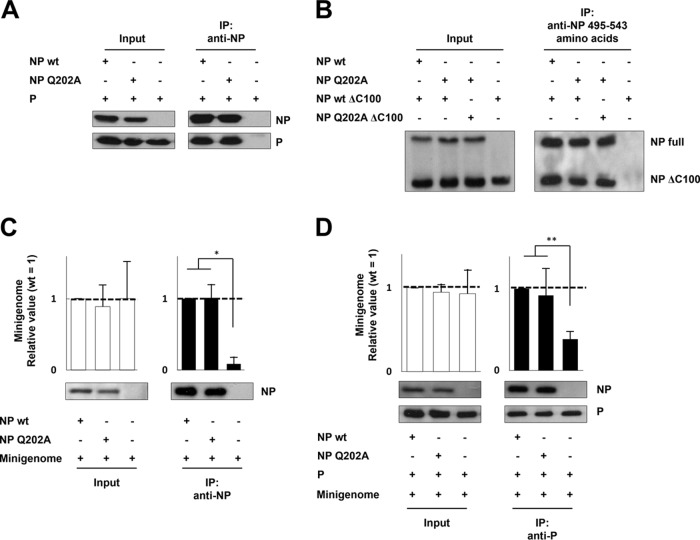
FIG 3.
Effects of NPQ202A on NP-P interaction, NP-NP self-interaction, and NP-RNA binding (A) Interaction between NP and P. BSR T7/5 cells transfected with NP- and P-expressing plasmids were subjected to IP assay using a mixture of anti-NP MAbs. Both NPwt and NPQ202A were detected by Western blotting using anti-NP MAb, and P was detected by anti-P/V MAb. (B) Interaction between NP and NPΔC100. BSR T7/5 cells transfected with NP- and NPΔC100-expressing plasmids were subjected to IP assay using a MAb against the C terminus of NP (MAb 159-1, which reacts with NP amino acids 495 to 543). NPwt, NPQ202A, NP(wt)ΔC100, and NP(Q202A)ΔC100 were detected by Western blotting using a MAb against N terminus of NP (MAb 330-1, which reacts with NP amino acids 1 to 100). (C) Interaction between NP mutants and the minigenome. BSR T7/5 cells transfected with NP- and minigenome-expressing plasmids were subjected to RNA IP assay using an anti-NP MAb. (D) Interaction between NP mutants and P in the form of the NP-RNA complex. BSR T7/5 cells transfected with P-, NP-, and minigenome-expressing plasmids were subjected to RNA IP assay using an anti-P/V MAb. The relative amounts of RNA were measured by qRT-PCR. Data represent means and standard deviations from triplicate experiments. Proteins were detected by Western blotting using anti-NP and -P/V MAbs. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.05.