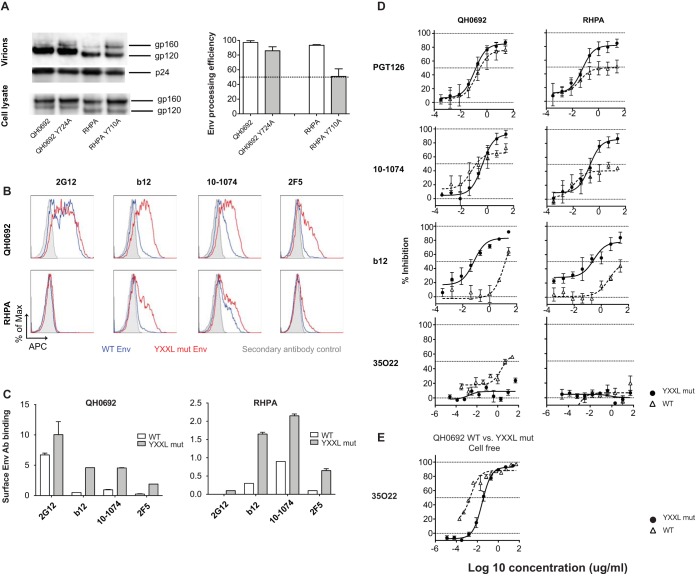
FIG 6.
Impact of mutation of the YXXL sorting motif on potency of antibody neutralization and maximum neutralization phenotype in both cell-associated and cell-free infection. (A) NLCI constructs with wild-type and YXXL mutant Env expression in transfected 293T cells and Env incorporation into viral particles were examined by Western blotting. The amount of sample loaded was normalized to the amount of p24 antigen as determined by ELISA. The processing efficiency of Env precursor gp160 was quantitated, and the data are shown in bar graphs. Error bars represent SEM of results from duplicates of at least two independent experiments conducted on different dates. (B) Jurkat cells were nucleofected with NLCIQH0692-Y724A, NLCIRHPA-Y710A,NLCIQH0692, and NLCIRHPA, and at 24 h after neucleofection, cells were stained for analysis of surface Env expression levels with MAb 2G12, b12, 10-1074, and 2F5 followed by Alexa Fluor 647 anti-human IgG. Gray shades in histograms represent secondary antibody control; blue and red lines represent wild-type strain and YXXL mutant (mut) surface Env staining, respectively. APC, allophycocyanin. (C) Surface Env binding with MAbs 2G12, b12, 10-1074, and 2F5 represented by the relative values of MFI, which is a ratio of the median MFI determined for Env-AF647 of mCherry-high cells to the MFI of secondary antibody control and was calculated as follows: relative MFI = (MFI Env-AF647 − MFI secondary antibody control)/MFI secondary antibody control. The relative values of MFI of the WT strain and YXXL mutants stained with different MAbs are shown in white and gray, respectively. (D) Mutants with a disrupted YXXL motif were tested for maximal percentage of inhibition by MAbs PGT126, 10-1074, b12, and 35O22 in cell-to-cell neutralization. (E) The WT strain and a YXXL mutant of NLCIQH0692 were tested and compared for neutralization sensitivity in cell-free infection with 35O22.