FIG 1.
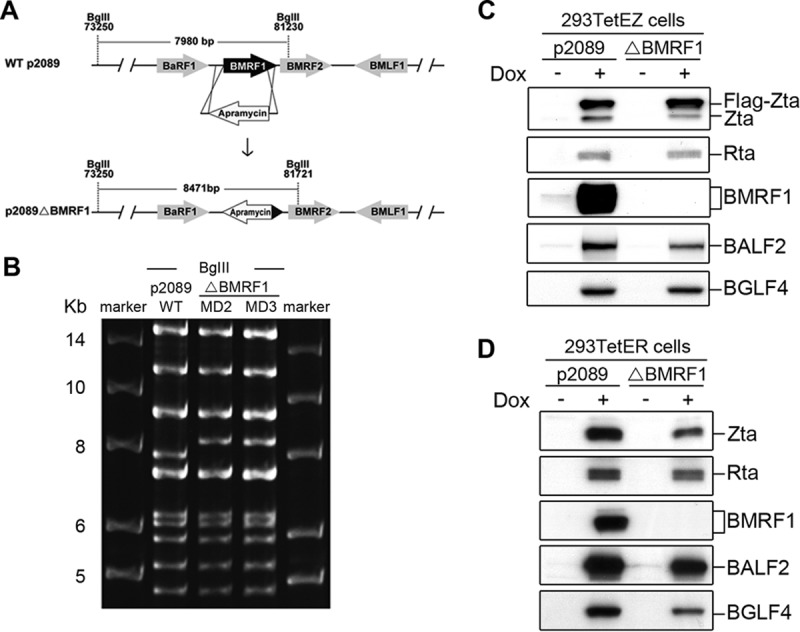
Construction of the BMRF1 knockout EBV bacmid and establishment of doxycycline-inducible bacmid 293TetEZ or 293TetER cell lines harboring WT or mutant bacmids. (A) To generate the Maxi-EBVΔBMRF1 bacmid, the BMRF1 open reading frame of Maxi-EBV p2089 was replaced with an apramycin-resistant gene by PCR targeting. After homologous recombination, the size of the BamHI M fragment was increased from 7,980 bp to 8,471 bp. (B) Maxi-EBV p2089 wild-type and p2089ΔBMRF1 bacmid DNAs were digested by BglII, and the genome patterns of the wild type and BMRF1 mutant were analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. (C and D) The wild-type p2089 or BMRF1 knockout bacmid was transfected into 293TetEZ or 293TetER cells and selected with hygromycin (50 μg/ml) for 1 month. Selected bacmid cell lines with similar copy numbers of viral genomes were treated with doxycycline (100 ng/ml) to induce lytic cycle progression. Cell lysates from p2089- and p2089ΔBMRF1-containing cells were harvested to detect lytic protein expression by Western blotting with the antibodies indicated.
