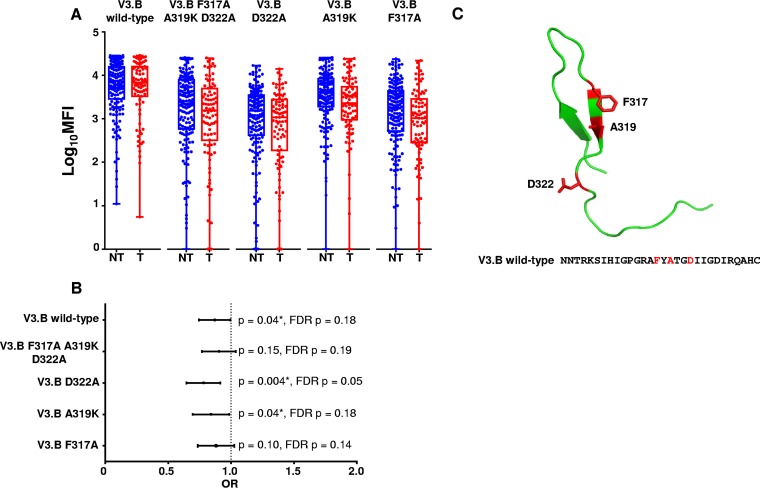
FIG 3.
Maternal plasma linear V3-specific IgG binding responses and MTCT risk against peptides with single amino acid residue substitutions. (A) Magnitudes of maternal plasma linear V3-specific IgG binding responses to V3.B wild type, V3.B F317A A319K D322R, V3.B D322R, V3.B A319K, and V3.B F317A. The V3-specific MAb CH22 was used as a positive control (mean MFIs at 5 μg/ml, 13,817, 25,241, 26,639, and 3,710 for V3.B F317A A319K D322A, V3.B D322A, V3.B A319K, and V3.B F317A, respectively) in NT (blue) and T (red) women. Normal human serum was used as a negative control (mean MFI at 1:500 dilution, 100). (B) Odds ratio plot of V3.B wild-type, V3.B triple-mutant, and V3.B single-mutant peptides. As the analysis was designed as a secondary, immune correlate analysis, significant raw P values are indicated by asterisks (P < 0.05). (C) Predicted structural locations of amino acid targets of maternal IgG responses associated with reduced MTCT risk. The HIV Env V3 loop with amino acid residue positions F317, A319, and D322, which are targeted by maternal plasma binding and neutralizing IgG responses associated with reduced MTCT risk, is shown in red. The V3 structure was generated using PyMOL.