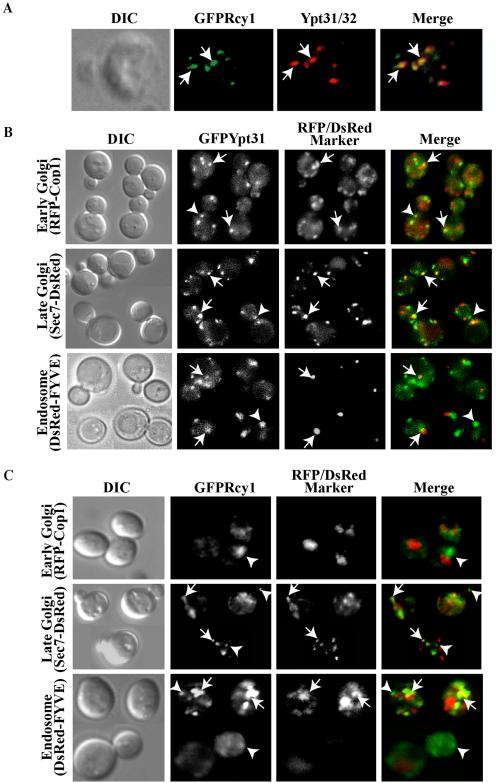
Figure 3.
Ypt31/32 colocalize with Rcy1, and they both reside on late Golgi and endosomes. (A) GFP-Rcy1 and Ypt31/32 colocalize. Wild-type cells (NSY125) expressing GFP-Rcy1 were grown at 26°C and synchronized using α-factor (see Materials and Methods). The cells were fixed and Ypt31/32 localization was viewed by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy by using affinity-purified anti-Ypt31/32 antibodies (red). GFP-Rcy1 was viewed using an FITC filter (green). (B) Ypt31 colocalizes with Golgi and endosomal markers. Cells expressing EGFP-Ypt31 and RFP-Cop1, Sec7-DsRED, or DsRED-FYVE were viewed by direct fluorescence microscopy. EGFP-Ypt31was viewed using an FITC filter (green) and RFP- or DsRed-tagged markers were viewed using a Texas Red filter (red). (C) Rcy1 colocalizes with late Golgi and endosomal markers. Cells expressing GFP-Rcy1 and RFP-Cop1, Sec7-DsRed, or DsRED-FYVE were viewed by direct fluorescence microscopy. GFP-Rcy1 was viewed using an FITC filter (green) and RFP- or DsRed-tagged markers were viewed using a Texas Red filter (red). The images in A, B, and C were deconvolved using a Zeiss Axioscope microscope. The merged image is shown on the right, and the contour of the cells is shown in the differential interference contrast (DIC) image. Arrows point to regions of colocalization, whereas arrowheads point to regions of Ypt31/32 or Rcy1 (green) that do not colocalize with the compartmental markers (red).