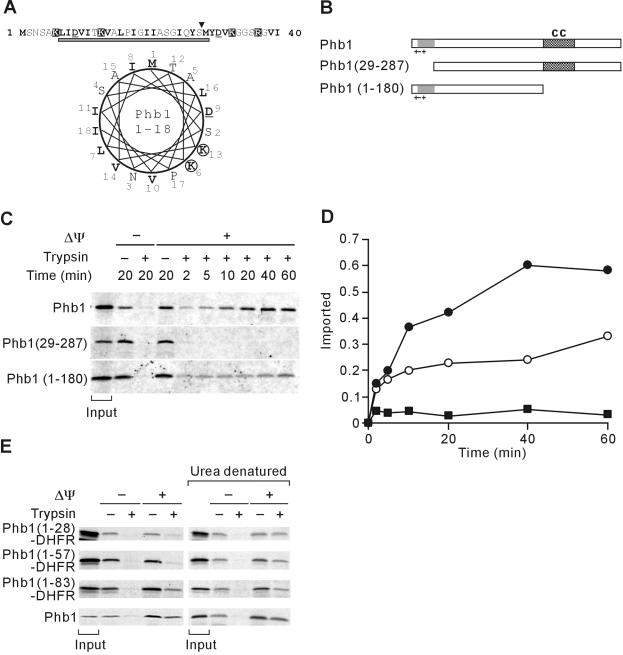
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial targeting of Phb1 by an unconventional N-terminal presequence. (A) N-terminal region of Phb1. Amino acid residues 1-40 of S. cerevisiae Phb1 and a helical wheel representation of amino acid residues 1-18 is shown and marked as in Figure 1A. The gray bar indicates a potential transmembrane region of Phb1 that is predicted with low scores by using the TMHMM program. (B) Schematic representation of Phb1 and derivatives. Symbols are as in Figure 1B. (C) Mitochondrial import of Phb1 and its variants. 35S-labeled precursor proteins were incubated with isolated mitochondria at 25°C for the indicated time in the presence (+Δψ) or absence (-Δψ) of a membrane potential. Nonimported proteins were digested with trypsin when indicated. The quantification of the import kinetics of Phb1 (•), Phb1(29-288) (▪), and Phb1(1-180) (○) is shown in D. Total radioactivity added to the import reaction is shown as “input” in C and was set to 1 in D. (E) Import of Phb1-DHFR hybrid proteins into mitochondria. 35S-labeled hybrid proteins were incubated with isolated mitochondria for 20 min at 25°C as in C. When indicated, hybrid proteins were precipitated with ammonium sulfate and urea-denatured before import. Signals corresponding to 20% of radiolabeled precursors incubated with mitochondria are shown (input).