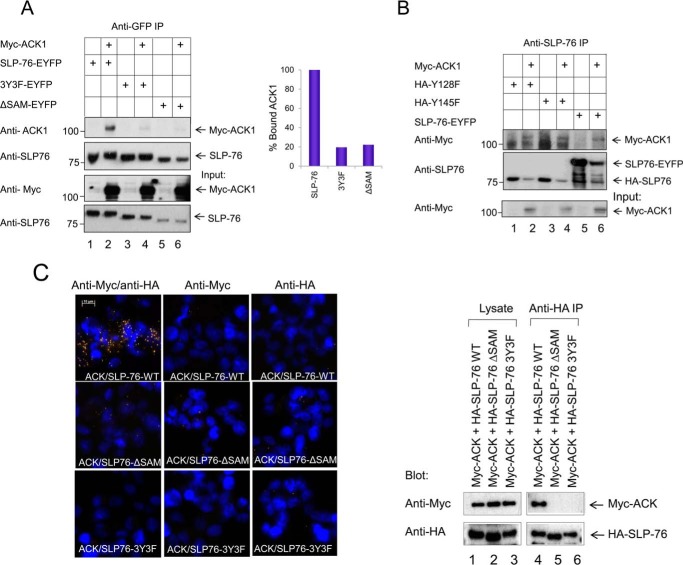
Figure 2.
ACK1 binding to SLP-76 is dependent on the SLP-76 SAM domain and three proximal tyrosine residues: Tyr-113, Tyr-128, and Tyr-145. A, ACK1 binding to the SLP-76 mutant in HEK293T cells. Various SLP-76 mutants (wild-type SLP-76, proximal tyrosine mutant (3Y3F), or SAM-deficient (ΔSAM) SLP-76) were expressed with Myc-tagged ACK1. Cells were transfected for 24 h before harvesting. Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-GFP antibody, capturing SLP-76 and bound ACK1 (lane 2). No binding was seen with ΔSAM (lane 6) or the 3Y3F mutant (lane 4). The percentage of bound ACK1 is shown in the right panel. B, unlike the 3Y3F mutant, the HA-tagged single tyrosine mutants Y128F and Y145F failed to disrupt the SLP76-ACK1 complex (lanes 2 and 4). C, left panel, in situ proximity ligation assay (PLA) showing co-localization of Myc-ACK1 with HA-SLP-76 (red dots, top row) but not with SLP76-ΔSAM (center row) or 3Y3F mutants (bottom row). No binding was seen in controls. Right panel, binding assessed by immunoprecipitation from the lysates of samples used in the PLA. The results in C are representative of two experiments and in A and B representative of four experiments performed in two different laboratories.