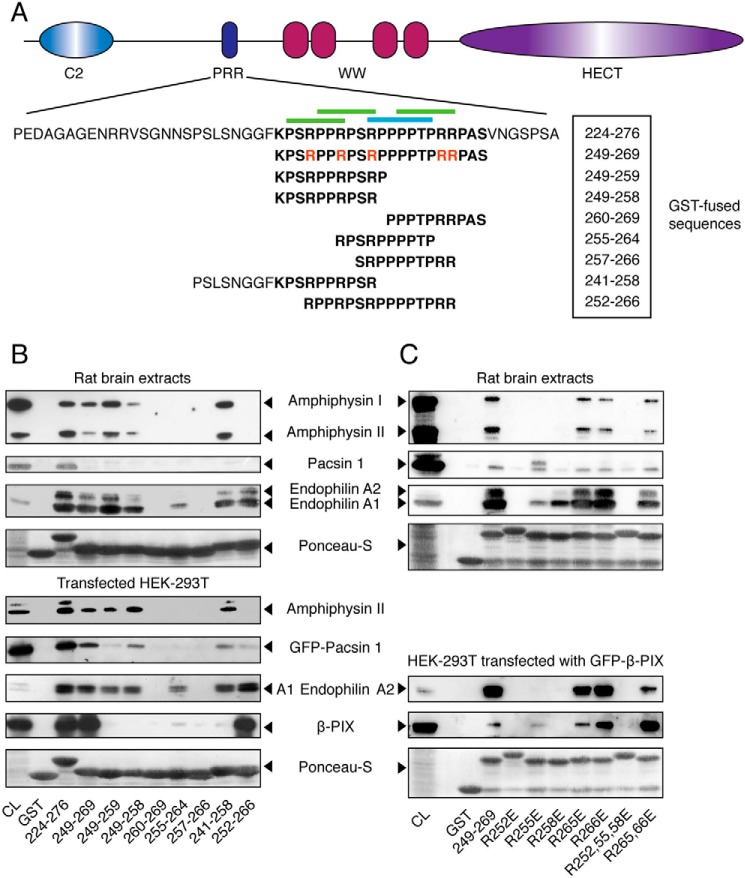
Figure 2.
Binding preferences of the SH3 domains of amphiphysin, pacsin, endophilin, and β-PIX toward the PRR of Itch. A, schematic representation of the Itch protein highlighting the sequence of the full-length PRR (boldface type) as well as the specific sub-sequences used in these studies. Arginine residues mutated to glutamic acid in the context of the 249–269 peptide are indicated in red. Canonical class I and II binding sites are indicated by blue and green overbars, respectively. B, rat brain extracts were incubated with the indicated GST-PRR fusions bound to GSH resin. Immunoblots of bound proteins eluted from the resin were performed with anti-amphiphysin, anti-pan-endophilin, and anti-pacsin 1 antibodies to show their content, and 5% of the cell lysates served as a control (CL) (top panels). Extracts from HEK-293T cells transfected with the indicated constructs were incubated with the same GST fusions bound to GSH resin. The immunoblots of bound proteins eluted from the resin were performed with anti-amphiphysin, anti-GFP (GFP-pacsin 1 and GFP-endophilin A1), or anti-FLAG (FLAG-β-PIX). Immunoblots were performed on 5% of cell lysates (CL) to determine protein overexpression levels (bottom panels). C, rat brain extracts were incubated with the indicated GST-PRR mutant bound to GSH resin. The immunoblots of the bound proteins eluted from the resin were performed as in B to determine endogenous protein expression in 10% of cell lysates (CL) and their recovery in the pulldown assay (top panels). Extracts from HEK-293T cells overexpressing GFP-β-PIX were incubated with the GST-PRR mutants bound to GSH resin. The immunoblots of bound proteins eluted from the resin were performed with anti-pan-endophilin or anti-GFP to measure the quantities of endogenous endophilin and transfected GFP-β-PIX recovered from the same cell lysate (bottom panels).