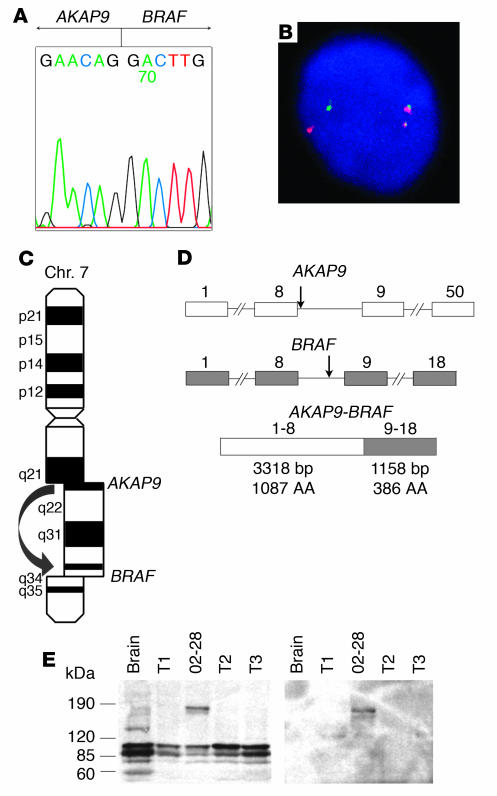
Figure 2.
BRAF is recombined with the AKAP9 gene and results in expression of a fusion protein. (A) Sequence of the 5′ RACE product showing a fusion point between AKAP9 and BRAF. (B) Confirmation of the reciprocal fusion by FISH with probes corresponding to the BRAF (red) and AKAP9 (green) genes. (C) The fusion is a result of paracentric chromosomal inversion inv(7)(q21–22q34). Chr., chromosome. (D) Genomic structure of the BRAF and AKAP9 genes showing the location of breakpoints (arrows) and the organization of the chimeric cDNA. Exons are represented by boxes and introns by lines. Numbers above indicate exon numbers. (E) Western blot analysis using BRAF antibody (left) and AKAP9 antibody (right), showing an approximately 170-kDa protein, corresponding to the predicted molecular weight of the fusion protein in the index case (number 02-28). Three other papillary carcinomas (T1–T3) are shown for comparison. Wild-type AKAP9 is 453 kDa in size and was not detected in this Western blot.