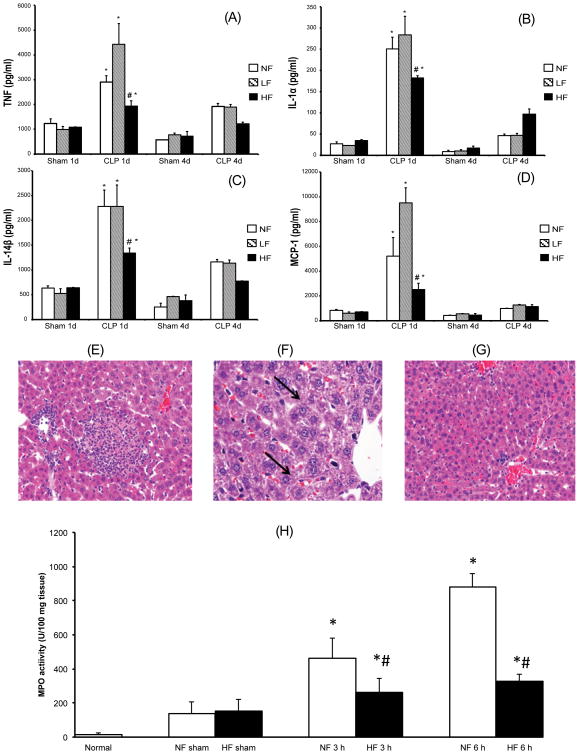
Figure 2.
Cellulose supplementation dampens the severity of systemic inflammation after cecal ligation and puncture. Shown are results for mice fed LF, NF and HF diets for two weeks prior to CLP or sham surgery. (A-D) Plasma concentrations at 1 day and 4 days after CLP are shown for TNFα (A), IL-1ɑ (B), IL-1β (C), and MCP-1 (D) are shown. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E.M. of 6 mice for each group. (*Represents P < 0.05 versus sham mice; # represents P < 0.05 versus mice fed with NF and LF diet and subjected to CLP) (E-G) Representative hepatic sections from NF, LF, and HF diet mice that were sacrificed 7 days after CLP. NF and LF diet mice demonstrate spotty hepatic necrosis, hemorrhage, neutrophilic infiltration and ballooning degeneration (E-F; bold arrows). In contrast, HF diet fed mice demonstrated a preservation of the hepatic architecture with infrequent necrosis, reduction in inflammatory cell infiltration and decreased ballooning degeneration (G). (H) MPO, an enzyme present in neutrophils, was measured as an index of neutrophil infiltration into the pulmonary tissue at 3 and 6 hours after CLP in the NF and HF diet mice. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E.M. of 6 mice for each group.(*Represents P < 0.05 versus sham mice; # represents P < 0.05 versus mice fed with NF and subjected to CLP).