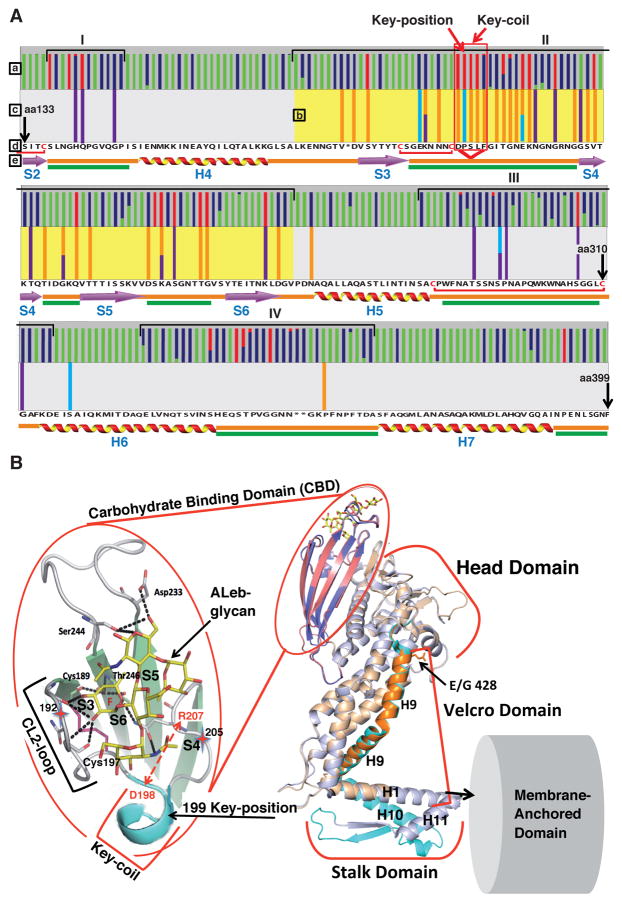
Figure 4. Amino Acid Replacements for Adaptation in Acid Sensitivity in Leb-Binding.
(A) The BabA CBD is under both positive and adaptive selection. Here, the BabA aa133–399 segment is shown with the Key-position and Key-coil (red vertical box) indicated in close proximity to the fucose-binding CL2 disulfide-clasped loop (red bracket). (a) The colored bars represent amino acid residues under positive selection, i.e. single nucleotide mutations that result in high level (red) or moderate level (blue) of amino acid substitutions or conservation (green) of amino acids (Aspholm-Hurtig et al., 2004). The high-level positive selection clusters are indicated as I–IV. (b) The pH50-dependent substitutions co-localize the strongest with Cluster II (CBD, aa175–255 (yellow)), but not with Cluster IV. (c) The series of pH50 substitutions in Greek strains (purple bars (Figure S4D)), SO-2 isolates (light-blue bars (Figure S3B)), and the GC-patient isolates (orange bars (Figure 6E)) are located in Clusters I–III. (d) The reference sequence is P448 BabA, and stars indicate positions missing in this strain’s BabA sequence (Aspholm-Hurtig et al., 2004). (e) Intrinsically unstructured regions (IUR) (green bars) were predicted by DisEMBL and GlobPlot. In BabA, the IUR segments join β-strands (lilac arrows) and α-helices (ribbons) and exhibit higher prevalence of polar amino acids and prolines for rapid and precise responses to changes in the local environment (Dyson and Wright, 2005; Rauscher et al., 2006).
(B) Structural organization of the CBD and Velcro Domain acid-sensitivity determinants. The CBD is carried by the Head Domain. The coiled-coil Stalk Domain connects the Head Domain with the predicted Membrane-Anchored Domain (Hage et al., 2015; Moonens et al., 2016). The four β-strands S3–S6 with IUR loops constitute the CBD along with the disulfide (C189/C197)-clasped (in magenta) fucose-binding loop CL2, which is immediately followed by the Key-coil (aa198–202) and Key-position (aa199) in most BabAs. D198 in the Key-coil forms a salt bridge with R207 that acts as a structural clamp (dashed red arrow). The salt bridge acts as a pH sensor and breaks open due to protonation of the aspartic acid at pH <4. H9 in the Head Domain and H1/10 in the Stalk Domain together comprise the Velcro Domain. The K192/D205 Exceptional (Ex) motif (red stars) seems to constitute an additional mechanism for increased acid sensitivity in binding.