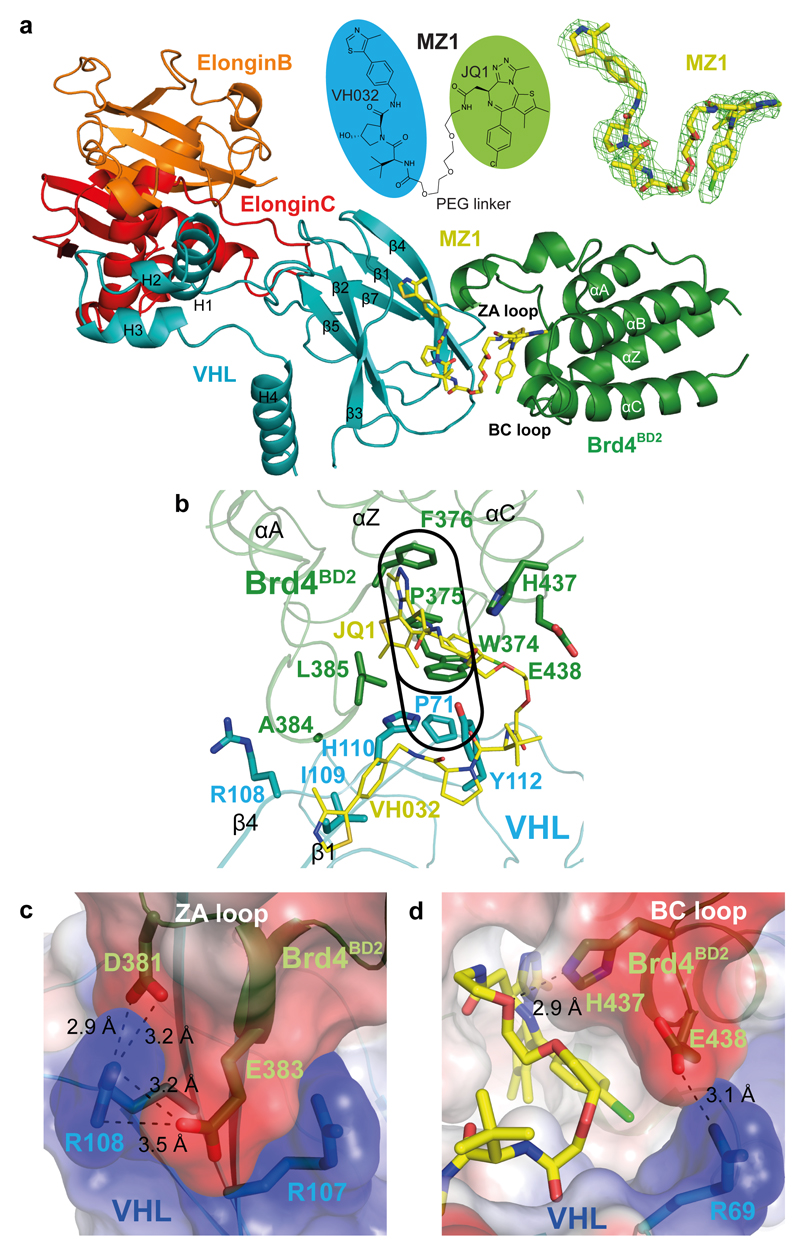
Figure 1. The crystal structure of the Brd4BD2:MZ1:VHL-ElonginC-ElonginB complex.
a, Overall structure of Brd4BD2:MZ1:VHL-ElonginC-ElonginB in ribbon representation. Top middle, chemical structure of bifunctional PROTAC molecule MZ1. Top right, Fo−Fc omit map generated prior to ligand modelling contoured at 3.0σ around bound MZ1. b, Key residues forming the hydrophobic “base” of the induced Brd4BD2:VHL interface. The "WPF" shelf of Brd4BD2 and extended "PWPF" stack are outlined in black. The JQ1 and VH032 elements of MZ1 are labelled in yellow. c, Electrostatic potential map showing the charged zipper contacts between Brd4BD2 residues D381 and E383 with VHL residues R107 and R108. d, Electrostatic potential map showing the interaction between Brd4BD2 residue E438 with VHL residue R69. The hydrogen bond between H437 of Brd4BD2 and the PEG linker of MZ1 is also shown. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds with distances shown in angstroms (Å).