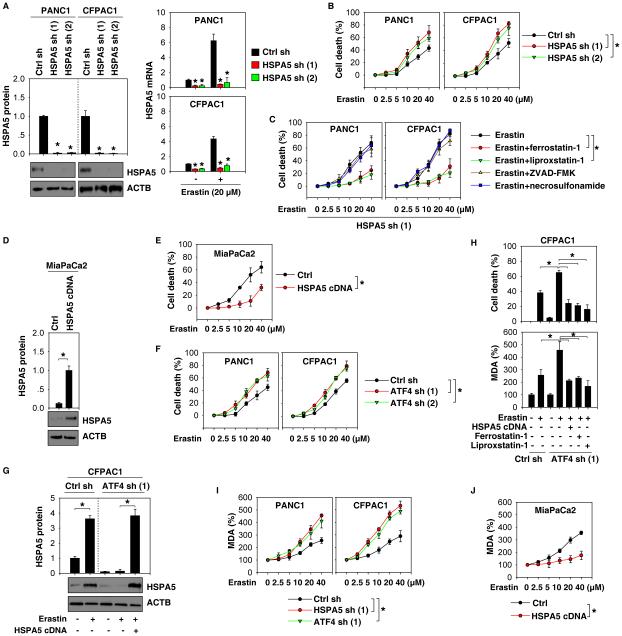
Figure 2. HSPA5 negatively regulates ferroptosis.
(A, B) Knockdown of HSPA5 by shRNA enhanced erastin-induced cell death in indicated PDAC cells at 24 hours (n=3, *p < 0.05 versus control shRNA group). (C) Indicated HSPA5 knockdown PDAC cells were treated with erastin (2.5-40 μM) with or without indicated inhibitors (ferrostatin-1, 1 μM; liprostatin-1, 1 μM; ZVAD-FMK, 10 μM; necrosulfonamide, 0.5 μM) for 24 hours. Cell death was assayed using a CCK8 kit (n=3, *p < 0.05). (D, E) Overexpression of HSPA5 by gene transfection of pcDNA3.1-HSPA5 cDNA inhibited erastin-induced cell death in MiaPaCa2 cells at 24 hours (n=3, *p < 0.05). (F) Knockdown of ATF4 by shRNA enhanced erastin-induced cell death in indicated PDAC cells at 24 hours (n=3, *p < 0.05). (G, H) Overexpression of HSPA5 (pcDNA3.1-HSPA5 cDNA) or treatment with ferroptosis inhibitors (ferrostatin-1, 1 μM; liprostatin-1, 1 μM) reversed erastin (20 μM, 24 hours)-induced cell death and MDA production in ATF4 knockdown CFPAC1 cells (n=3, *p < 0.05). (I, J) Knockdown of HSPA5 or ATF4 increased erastin-induced MDA production in PANC1 and CFPAC1 cells (I), whereas overexpression of HSPA5 (pcDNA3.1-HSPA5 cDNA) limited erastin-induced MDA production at 24 hours in MiaPaCa2 cells (J) (n=3, *p < 0.05).