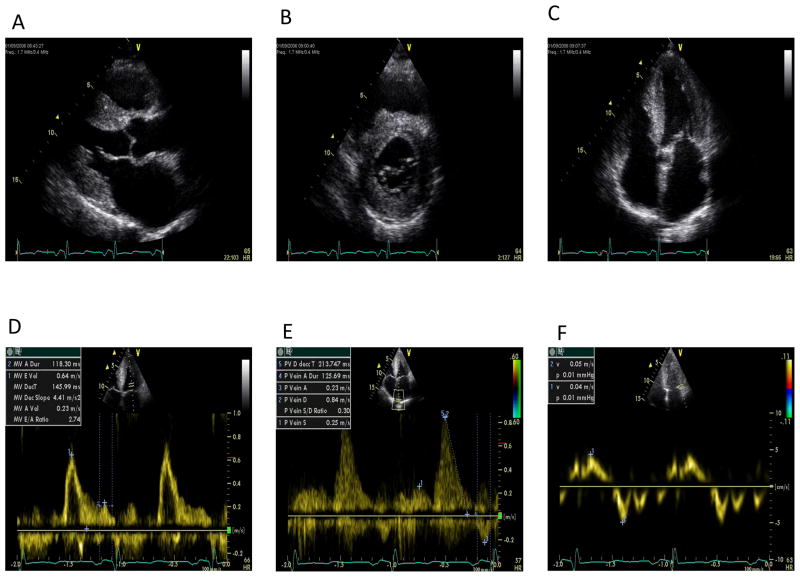
Figure 2.
Sequence of still images showing typical echocardiographic features of cardiac amyloidosis. A: 2-D Parasternal long axis showing concentric left ventricular hypertrophy, bright myocardium and left atrial dilatation. B: 2-D Parasternal short axis showing concentric left ventricular hypertrophy and bright myocardium. C: 2-D Apical four chamber view showing concentric left ventricular hypertrophy and biatrial dilatation D: Pulsed wave Doppler of mitral inflow showing an increase in E/A ratio, normal E wave deceleration time but a marked reduction in transmitral A wave velocity. E: Pulsed wave Doppler of pulmonary vein inflow showing marked diastolic prominence and increased duration and peak velocity of atrial reversal compared to the transmitral signal. F: Pulsed tissue Doppler of the lateral mitral annulus showing marked reduction in apical systolic and diastolic velocities (normal velocities being: >6 cm/sec and >8 cm/sec, respectively). Images courtesy of Professor Elliott, University College London, UK