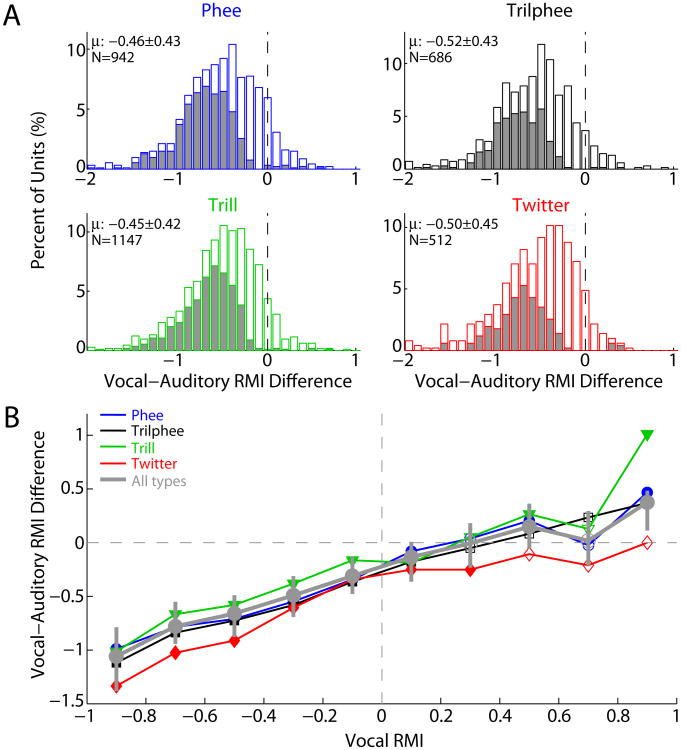
Fig. 4.
Distribution of vocal-auditory differences. A: Histograms are plotted showing the distribution of RMI differences between vocalization and playback (vocal - auditory) for each unit. Most units showed large shifts towards negative values, indicating suppression. Shaded bars: units with statistically significant differences between vocal production and playback (p<0.05, ranksum). B: Plot of mean vocal-auditory differences for units binned by vocal RMI. Differences were nearly zero for excited units, indicating matched vocal and auditory responses. Differences were negative for units with vocal RMI near zero, indicating that these vocal “unresponsive” units were actually suppressed compared to playback Colors indicate vocalization types as in A. Grey: average response including all vocalization types. Error bars: bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals. Filled symbols: statistically significant deviations from 0 (p<0.01. signed-rank).