Fig. 3.
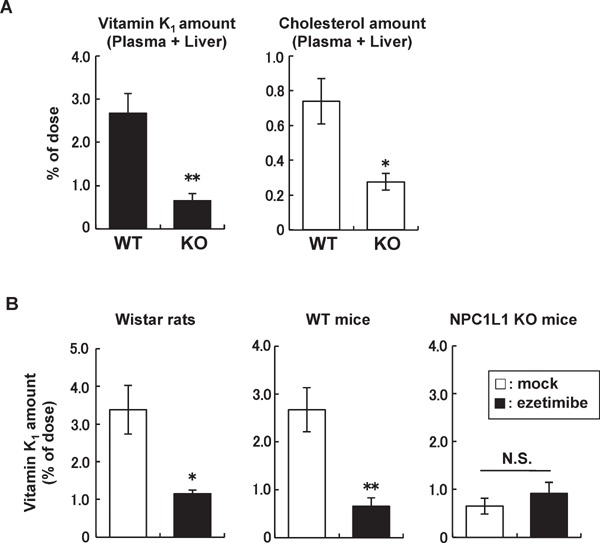
Intestinal vitamin K1 absorption in rodents.
(A) Intestinal absorption of vitamin K1 and cholesterol was examined in wild-type (WT) mice and NPC1L1 knockout (KO) mice. Vitamin K1 and [3H]cholesterol concentrations in the plasma and liver were examined 2 h after the intraduodenal administration of a vitamin K1- or [3H]cholesterol-containing emulsion. (B) Vitamin K1 absorption was examined in Wistar rats, WT mice, and NPC1L1 KO mice treated with or without ezetimibe (0.3 mg/kg for rats or 0.45 mg/kg for mice). Vitamin K1 concentrations in the plasma and liver were examined 3 h (for rats) or 2 h (for mice) after the intraduodenal administration of a vitamin K1-containing emulsion. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 4–8). **Significantly different by Student's t test (p < 0.01). *Significantly different by Student's t test (p < 0.05). N.S., not significantly different. (Modified and cited from reference 42).
