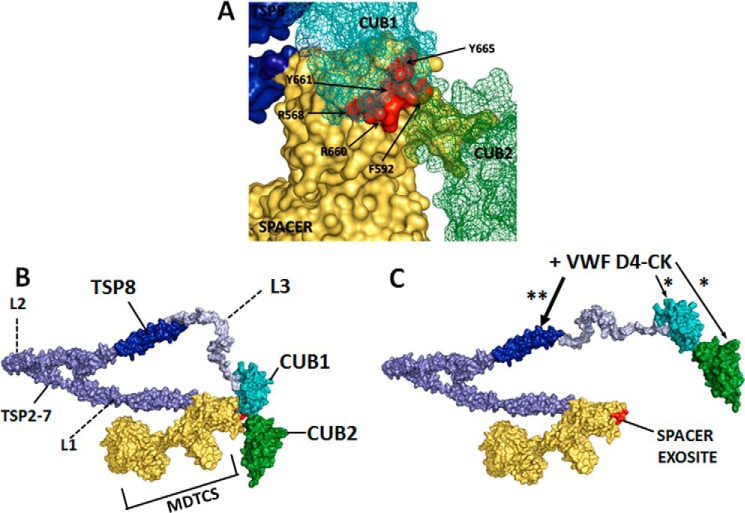
Figure 6.
The proposed mechanism of ADAMTS13 conformational activation. A, the CUB-spacer domain interface within a three-dimensional model of ADAMTS13. The spacer domain exosite 3 residues, mutated in the GoF ADAMTS13 variant, are indicated and shown in red. B, the closed conformation of ADAMTS13 showing the relative positions of the N-terminal domains MDTCS and the C-terminal CUB domains. Folding of the TSP2–8 domains is facilitated by the three flexible linker regions between TSP2 and TSP3 (L1), between TSP4 and TSP5 (L2), and between TSP8 and CUB1 (L3). C, moderate affinity interactions (*) between the D4-CK domains of VWF and CUB1/CUB2 serve to orientate VWF. As the binding interaction (**) occurs between TSP8 and the D4-CK domains of VWF, the rigid structure of the D4-CK domains causes a repositioning of the CUB domains at the L3 linker region. In the open conformation of ADAMTS13 the spacer domain exosite is exposed, in preparation for VWF A2 domain unfolding. The three-dimensional model of ADAMTS13 was constructed using the DTCS crystal structure (PDB 3GHM; Ref. 39), homology modeling of the MP-Dis domains, homology modeling of the CUB domains, and the thrombospondin-1 (TSP) type 1 repeat crystal structure (PDB 1LSL; Ref. 40).