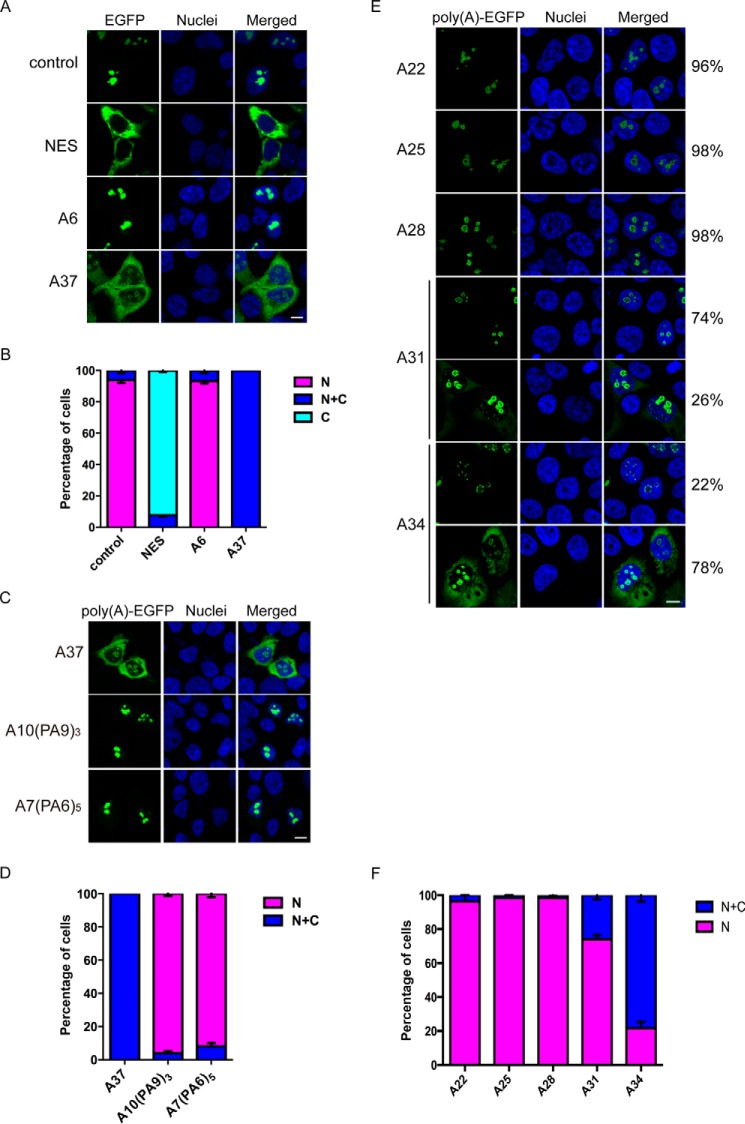
Figure 1.
Continuous expanded poly(A) tract alters the localization of nuclear proteins. A, subcellular localization of Rev(1.4)-poly(A)-EGFP proteins in HEK293 cells. The Rev(1.4)-EGFP control protein localized to the nuclear compartment, whereas the positive control Rev(1.4)-NES-EGFP (NES), which contained a functional HIV-1 Rev NES sequence, localized to the cytoplasm. The Rev(1.4)-poly(A)-EGFP protein with a 6-alanine tract (A6) localized in the nuclear compartment, whereas that with a 37-alanine tract Rev(1.4)-A37-EGFP (A37) showed both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, statistical analysis of A. C, subcellular localization of Rev(1.4)-polyAPA-EGFP proteins in HEK293 cells. The Rev(1.4)-A37-EGFP (A37) showed both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization, two Rev(1.4)-polyAPA-EGFP variants (A10(PA9)3 and A7(PA6)5) localized in the nuclear compartment. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342. Scale bar, 10 μm. D, statistical analysis of C. E, subcellular localization of Rev(1.4)-poly(A)-EGFP protein with A22, A25, A28, A31, and A34. A22, A25, and A28 showed nuclear localization. A31 resulted in 26% of cells with both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization, whereas A34 resulted in up to 78% of cells with both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization. Scale bar, 10 μm. F, statistical analysis (E). N, nuclear; C, cytoplasmic; C + N, cytoplasmic and nuclear localization. Three independent transfection experiments were performed. At least 100 transfected cells were analyzed in each experiment. Error bars, S.E.