Figure 1. Crystal structures of Glo qRRM1, qRRM2 and qRRM3 domains identify RNA-binding motifs.
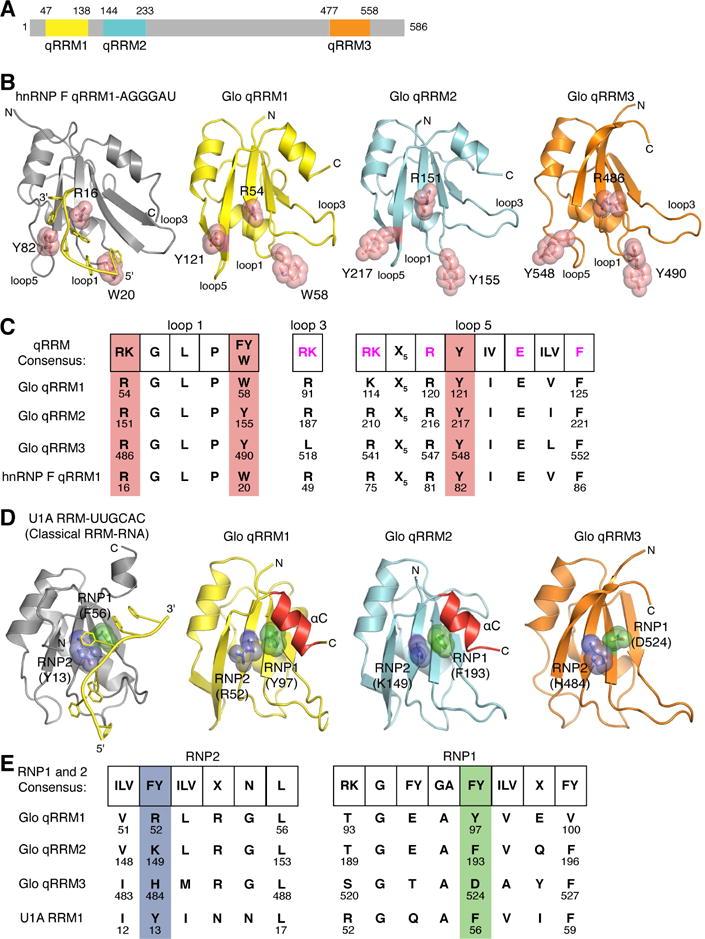
(A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of Glo. Amino acid residues at domain boundaries are numbered, and the qRRM domains are color coded: qRRM1 (yellow), qRRM2 (cyan) and qRRM3 (orange). (B) Ribbon diagrams of the solution structure of hnRNP F qRRM1 bound to single-stranded G-tract RNA (PDB code 2KFY; Dominguez et al., 2010) and crystal structures of Glo qRRMs. The ribbon diagram of hnRNP F qRRM1 is shown in grey with a cartoon representation of bound G-tract RNA in yellow. Three critical G-tract binding residues in hnRNP F qRRM1 are displayed as stick models superimposed with transparent red space-filling spheres (R16, W20, and Y82); the structurally equivalent residues in Glo qRRM1 (yellow), qRRM2 (cyan), and qRRM3 (orange) are displayed similarly. N- and C-termini of proteins, 5′ and 3′ ends of G-tract RNA, and loops 1, 3, and 5, which contain residues that may interact with G-tract RNA, are indicated. (C) Conservation of G-tract RNA-binding residues in Glo. Comparison of the consensus G-tract binding motif sequence of hnRNP F qRRMs with corresponding residues in Glo qRRMs and hnRNP F qRRM1. Consensus residues important for stacking interaction with G-tract RNA (shown in B) are highlighted in red. Additional residues involved in G-tract RNA binding are colored magenta in the consensus sequence. (D) Ribbon diagrams of the crystal structures of classical U1A RRM bound to a fragment of U1 small nuclear RNA (PDB code 1URN;(Oubridge et al., 1994) and Glo qRRMs. The ribbon diagram of U1A RRM is shown in grey with a cartoon representation of bound U1 small nuclear RNA sequence in yellow. Critical residues within the RNP1 and RNP2 motifs of U1A are displayed as stick models superimposed with transparent green and blue space-filling spheres, respectively (Y13 and F56); the structurally equivalent residues in Glo qRRM1, qRRM2, and qRRM3 are displayed similarly. αC helices in qRRM1 and qRRM2 that occlude the RNP1 motif are colored red. N- and C-termini of proteins and 5′ and 3′ ends of the fragment of U1 small nuclear RNA are indicated; the 5′ end of the RNA is truncated in this rendering. (E) Conservation of classical RRM RNA-binding residues in Glo. Comparison of the consensus RNP motif sequences of classical RRMs with corresponding residues in Glo qRRMs and U1A RRM. Consensus RNP1 and RNP2 residues important for RNA binding by classical RRMs are colored green and blue, respectively. See also Table S1.
