Figure 7. Regulation of chromosome dispersion and dorsal-ventral patterning are mediated solely by the G-tract binding mode of Glo.
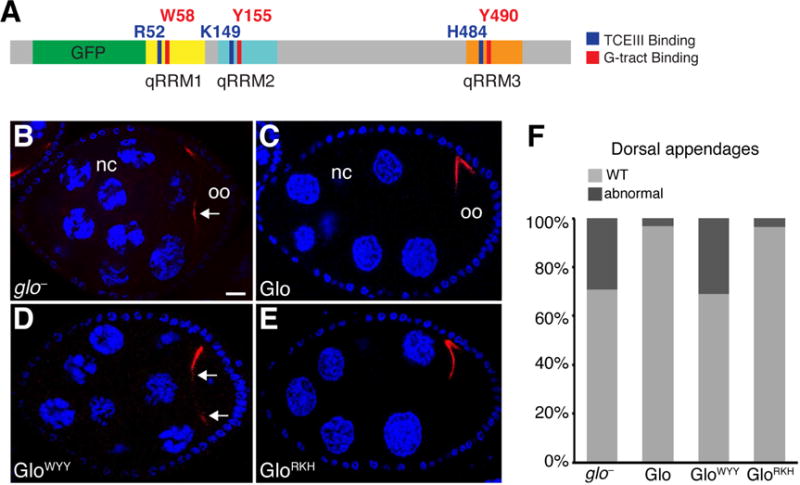
(A) Schematic representation of the GFP-Glo protein with a summary map of the alanine substitutions shown in Figure 5B, C and analyzed in (B–F). (B–E) Confocal sections of a glo mutant egg chamber (B) and glo mutant egg chambers expressing GFP-Glo (B), GFP-GloWYY(C), or GFP-GloRKH (D). Nurse cells (nc) and oocyte (oo) are indicated. grk mRNA (red) is detected by smFISH, nurse cell and follicle cell nuclei (blue) are stained with DAPI. Egg chambers are oriented with anterior to the left, dorsal up. Arrows indicate mislocalized grk mRNA. Scale bar=10 μM. (F) Quantification of the fraction of eggs laid by glo mutant females expressing GFP-Glo, GFP-GloWYY, or GFP-GloRKH that show dorsal appendage defects, including shortened, laterally expanded, fused, and/or missing appendages. See also Figures S5 and S6.
