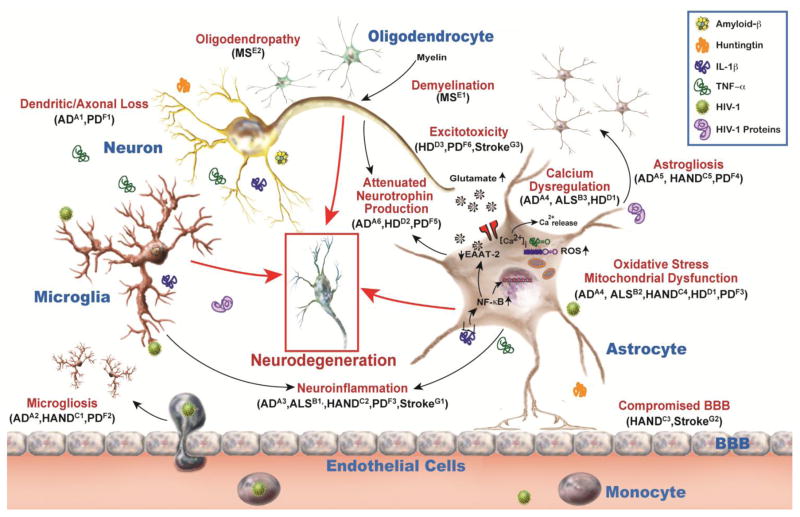
Fig. 1. Common cellular mechanisms implicated in neurological diseases and disorders (NDDs).
NDDs are associated with cellular dysfunctions of principal CNS cells including neurons, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes. Neuronal damage includes dendritic and axonal loss, and reduced neurotrophin secretion. Microglial activation occurs during brain injury and resultant proinflammatory cytokines induce neuroinflammation along with microgliosis due to extravasation of peripheral monocytes. Oligodendrocyte dysfunctions include demyelination and oligodendropathy, i.e. death of oligodendrocytes. During injury, astrocytes contribute to excitotoxicity, and neuroinflammation by reduced glutamate uptake and increased release of proinflammatory cytokines, respectively. They likely undergo oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, calcium dysregulation, attenuated neurotrophin production and astrogliosis. Additionally, altered BBB permeability can increase neuroinflammation and contribute to disease. These mechanisms precede or succeed neurodegeneration and overlap in diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [A1(Uylings and De Brabander, 2002), A2 (Wake et al., 2013), A3 (Wyss-Coray and Rogers, 2012), A4 (Alberdi et al., 2013), A5 (Fuller et al., 2009), A6 (Allen and Barres, 2009)], Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) [B1 (Evans et al., 2013), B2 (Manfredi and Xu, 2005), B3 (Grosskreutz et al., 2010)], HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) [C1 (Lu et al., 2011), C2 (Cisneros and Ghorpade, 2012), C3 (Persidsky et al., 2000), C4 (Steiner et al., 2006), C5 (Vartak-Sharma et al., 2014)], Huntington’s disease (HD) [D1 (Wang et al., 2013), D2 (Giralt et al., 2010), D3 (Fan and Raymond, 2007)], Multiple Sclerosis (MS) [E1 (Franklin and Kotter, 2008), E2 (Popescu and Lucchinetti, 2012)], Parkinson’s disease (PD) [F1 (Van Spronsen and Hoogenraad, 2010), F2 (Hu et al., 2008), F3 (Zinger et al., 2011), F4 (Niranjan, 2014), F5 (Drinkut et al., 2012), F6 (Ambrosi et al., 2014)], and stroke [G1 (Ceulemans et al., 2010), G2 (Xia et al., 2004), G3 (Lai et al., 2014)].