Figure 3.
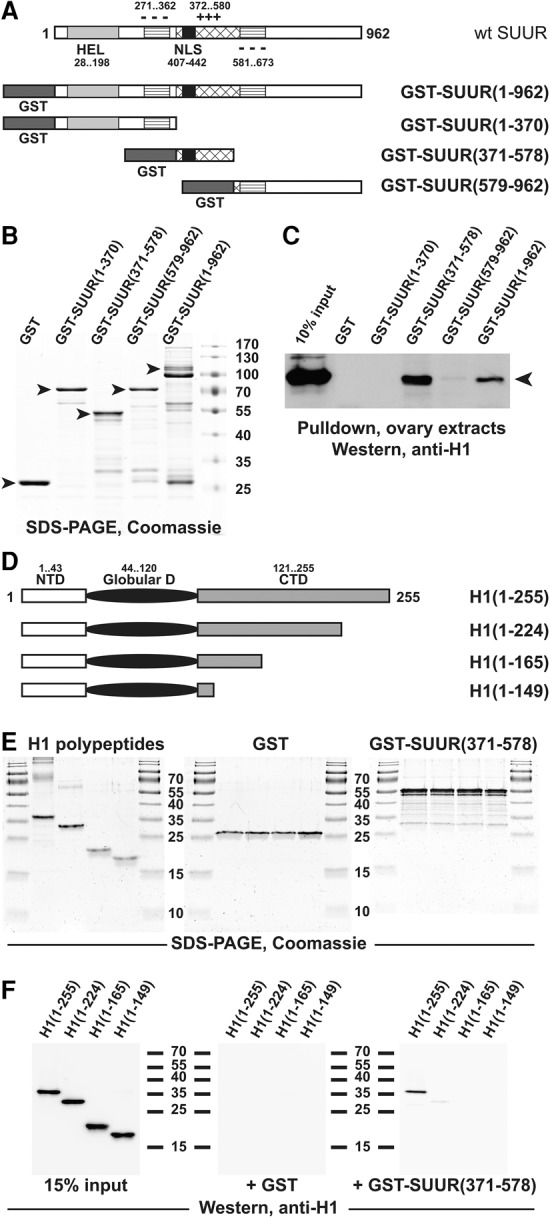
H1 and SUUR proteins exhibit direct physical interactions. (A) Schematic representation of GST-SUUR fusion expression constructs used for the analyses. The major structural domains of wild-type SUUR protein (open rectangle) are represented by light-gray (ATPase/helicase domain [HEL]), striped (negatively charged domain [−−−]), cross-hatched (positively charged domain [+++]), and black (NLS) boxes. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. N-terminal GST (dark-gray boxes) fusion constructs were prepared with full-length and the indicated truncations of SUUR. (B) Recombinant GST-SUUR fusion polypeptides. GST and GST fusion proteins (as in A) were expressed and purified from Escherichia coli, incubated with ovarian extracts, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. Arrowheads indicate full-length polypeptide products; molecular mass marker sizes (in kilodaltons) are shown at the right. (C) SUUR-dependent GST pull-downs of endogenous H1 from Drosophila ovarian extracts. Whole-cell extracts from adult Drosophila ovaries were incubated with GST fusion proteins (B), and pull-down products were analyzed by H1-specific immunoblot along with the 10% input control. Endogenous native H1 (arrowhead) strongly interacts with full-length and the middle fragment (amino acids 371–578) of recombinant SUUR. (D) Schematic representation of recombinant H1 polypeptides used for the analyses. The three major structural domains of Drosophila H1 are represented by an open rectangle (N-terminal domain [NTD]), a filled oval (GD), and a shaded rectangle (C-terminal domain [CTD]). Numbers indicate amino acid residues. Recombinant untagged full-length H1 and its indicated C-terminal truncations were expressed and purified from E. coli. (E) Recombinant polypeptides used for in vitro GST pull-down experiments. Recombinant GST (middle panel) and GST-SUUR(371–578) fusion protein (right panel) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining; the protein loading is equivalent to that in F. (Left panel) Recombinant H1 polypeptides were analyzed similarly; the protein loading is approximately sevenfold higher than that in the corresponding panel of F. Molecular mass marker sizes (in kilodaltons) are shown between the panels. (F) SUUR-dependent in vitro GST pull-downs of recombinant H1 polypeptides. The indicated H1 polypeptides were incubated with GST and GST-SUUR(371–578) fusion proteins, and pull-down products were analyzed by H1-specific immunoblot along with the 15% input control. Full-length H1 but not any of its C-terminal truncations strongly interacts with SUUR(371–578).
