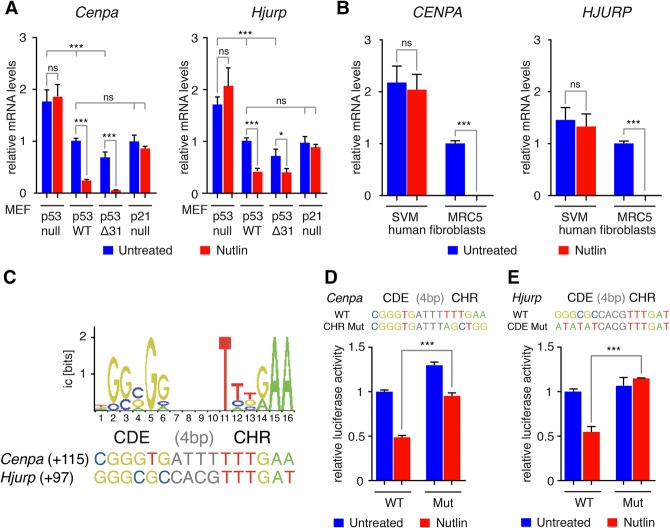
Figure 2.
Cenpa and Hjurp are down-regulated upon p53 activation. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of CENP-A and HJURP mRNA levels in p53-null, wild-type (WT), p53Δ31/Δ31 (Δ31), or p21-null MEFs untreated or treated with 10 µM nutlin for 24 h. Results from three (or two for p21-null) independent experiments are shown, each quantified in triplicate. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of CENP-A and HJURP mRNA levels in normal human fibroblasts (MRC5) or their SV40 transformed derivative cells (SVM for SV40 MRC5) in which p53 is inactive untreated or treated with 10 µM nutlin for 24 h. Results from three experiments are shown, each quantified in triplicate. (C) Putative CDE/CHR motifs identified near the transcription start sites (TSSs) of Cenpa and Hjurp using the positional frequency matrix (shown at the top; for details see Supplemental Fig. 2). Candidate CDE/CHR motifs were found close to the TSS of each gene; numbers in parentheses are positions relative to TSS. For Cenpa the CHR element perfectly matches the consensus sequence, whereas the CDE element perfectly matches the consensus sequence for Hjurp. (D,E) A 2-kb-long fragment centered around the Hjurp and Cenpa TSS, respectively, containing a wild-type or mutant CHR motif (for Cenpa) or CDE motif (for Hjurp) was cloned upstream of a luciferase gene and transfected into NIH/3T3 cells. The putative CDE/CHR and its mutated counterpart are shown. Nutlin treatment for 24 h induces a strong decrease in luciferase activity only with the construct containing a wild-type CDE/CHR motif. Data from two independent experiments (each in duplicates) were normalized, and the average luciferase activity in untreated cells transfected with the wild-type promoter construct was assigned a value of 1. For all graphs, means + SEM are shown. (***) P ≤ 0.001; (*) P ≤ 0.05; (NS) not significant, by ANOVA or Student's t-tests.