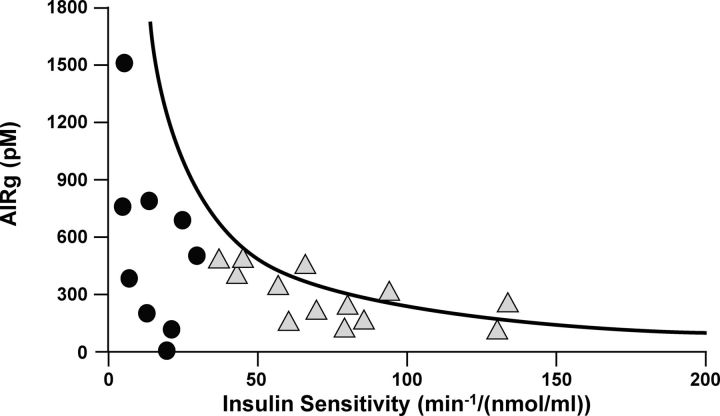
Figure 12.
β-Cell dysfunction in PCOS. Under normal circumstances, there is a compensatory increase in insulin secretion when insulin sensitivity decreases. This hyperbolic relationship is known as the DI. The majority of women with PCOS fall below the normal curve determined in concurrently studied age- and weight-comparable control women as well as normative data in the literature (292), which places them at increased risk for T2D. DI is decreased independent of obesity. Insulin secretion was determined as AIRg and insulin sensitivity by minimal model analysis of FSIGT glucose and insulin data. Circles, Obese PCOS; triangles, lean PCOS. [Adapted from A. Dunaif and D. T. Finegood: β-Cell dysfunction independent of obesity and glucose intolerance in the polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:942–947, 1996 (301) with permission. © The Endocrine Society.]