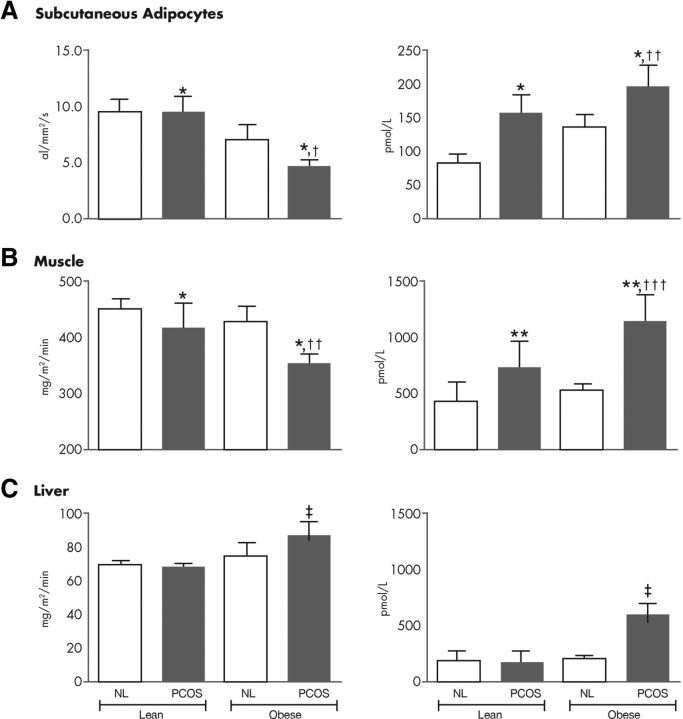
Figure 8.
Insulin action in isolated sc adipocytes and in vivo. The dose-response of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake was determined in isolated sc adipocytes in vitro and in vivo during sequential multiple insulin dose euglycemic glucose clamp studies. Maximal rates of glucose uptake (insulin responsiveness) in isolated sc adipocytes are depicted in vitro (A, left) and in vivo, which reflects primarily skeletal muscle glucose uptake (B, left). Rates of postabsorptive endogenous glucose production (EGP) (C, left) and its suppression by insulin were also assessed during the euglycemic glucose clamp study. The ED50 insulin (insulin sensitivity) for stimulation of glucose uptake and suppression of EGP are depicted in the graphs on the right (A, sc adipocytes in vitro; B, in vivo; C, EGP). Women with PCOS, gray bars; normal control women (NL), open bars. A two-way ANOVA with PCOS and obesity as factors was applied: *, P < 0.01 PCOS groups vs. NL groups; †, P < 0.05 obese groups vs. lean groups; ††, P < 0.01 obese groups vs. lean groups; †††, P < 0.001 obese groups vs. lean groups; ‡, P < 0.05 interaction PCOS and obesity. [Adapted from data published in A. Dunaif et al.: Evidence for distinctive and intrinsic defects in insulin action in polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes 41:1257–1266, 1992 (192), with permission. © American Diabetes Association.]