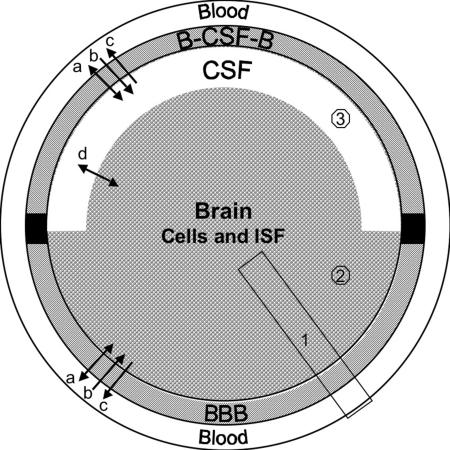
FIG. 1.
The interfaces between CNS and systemic blood: BBB is formed by microvascular endothelial cells. B-CSF-B is formed by the choroid plexus epithelial cells, which also secrete CSF. Transport processes at both barrier systems include (a) passive exchange via transcellular or paracellular diffusion, (b) uptake by facilitative or active carriers and receptor-mediated transport, (c) active efflux. In (d) there is exchange by diffusion and bulk flow between brain interstitial fluid (ISF) and CSF, which are not separated by a tight cellular barrier. In vivo methods for measurement of brain uptake differ in the sampling compartment: 1) whole tissue samples include vascular content, vasculature, brain cells and interstitial fluid, 2) microdialysis methods sample interstitial fluid, and 3) catheters in ventricles or subarachnoid space collect CSF.